Page 243 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 243
Plate 9-3 Genodermatoses and Syndromes
MANIFESTATIONS OF BASAL CELL NEVUS SYNDROME
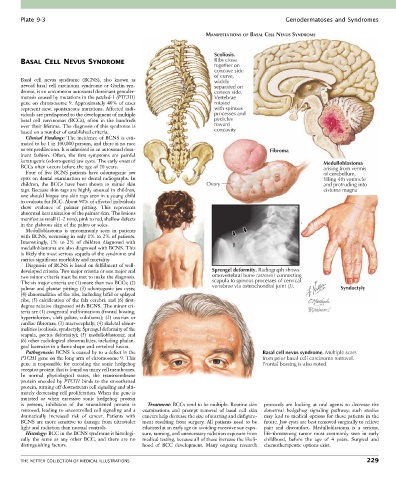
Scoliosis.
BASAL CELL NEVUS SYNDROME Ribs close
together on
concave side
of curve,
Basal cell nevus syndrome (BCNS), also known as widely
nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or Gorlin syn- separated on
drome, is an uncommon autosomal dominant genoder- convex side.
matosis caused by mutations in the patched-1 (PTCH1) Vertebrae
gene on chromosome 9. Approximately 40% of cases rotated
represent new, spontaneous mutations. Affected indi- with spinous
viduals are predisposed to the development of multiple processes and
basal cell carcinomas (BCCs), often in the hundreds pedicles
over their lifetime. The diagnosis of this syndrome is toward
based on a number of established criteria. concavity
Clinical Findings: The incidence of BCNS is esti-
mated to be 1 in 100,000 persons, and there is no race
or sex predilection. It is inherited in an autosomal dom- Fibroma
inant fashion. Often, the first symptoms are painful
keratogenic (odontogenic) jaw cysts. The early onset of Medulloblastoma
BCCs often occurs before the age of 20 years. arising from vermis
Four of five BCNS patients have odontogenic jaw of cerebellum,
cysts on dental examination or dental radiographs. In filling 4th ventricle
children, the BCCs have been shown to mimic skin Ovary and protruding into
tags. Because skin tags are highly unusual in children, cisterna magna
one should biopsy any skin tags seen in a young child
to evaluate for BCC. About 90% of affected individuals
show evidence of palmar pitting. This represents
abnormal keratinization of the palmar skin. The lesions
manifest as small (1-2 mm), pink to red, shallow defects
in the glabrous skin of the palms or soles.
Medulloblastoma is uncommonly seen in patients
with BCNS, occurring in only 1% to 2% of patients.
Interestingly, 1% to 2% of children diagnosed with J
medulloblastoma are also diagnosed with BCNS. This
is likely the most serious sequela of the syndrome and
carries significant morbidity and mortality.
Diagnosis of BCNS is based on fulfillment of well-
developed criteria. Two major criteria or one major and Sprengel deformity. Radiograph shows
two minor criteria must be met to make the diagnosis. omovertebral bone (arrows) connecting
The six major criteria are (1) more than two BCCs; (2) scapula to spinous processes of cervical
palmar and plantar pitting; (3) odontogenic jaw cysts; vertebrae via osteochondral joint (J). Syndactyly
(4) abnormalities of the ribs, including bifid or splayed
ribs; (5) calcification of the falx cerebri; and (6) first-
degree relative diagnosed with BCNS. The minor cri-
teria are (1) congenital malformations (frontal bossing,
hypertelorism, cleft palate, coloboma); (2) ovarian or
cardiac fibromas; (3) macrocephaly; (4) skeletal abnor-
malities (scoliosis, syndactyly, Sprengel deformity of the
scapula, pectus deformity); (5) medulloblastoma; and
(6) other radiological abnormalities, including phalan-
geal lucencies in a flame shape and vertebral fusion.
Pathogenesis: BCNS is caused by to a defect in the Basal cell nevus syndrome. Multiple scars
PTCH1 gene on the long arm of chromosome 9. This from prior basal cell carcinoma removal.
gene is responsible for encoding the sonic hedgehog Frontal bossing is also noted.
receptor protein that is found on many cell membranes.
In normal physiological states, the transmembrane
protein encoded by PTCH1 binds to the smoothened
protein, turning off downstream cell signaling and ulti-
mately decreasing cell proliferation. When the gene is
mutated or when excessive sonic hedgehog protein
is present, inhibition of the smoothened protein is Treatment: BCCs tend to be multiple. Routine skin protocols are looking at oral agents to decrease the
removed, leading to uncontrolled cell signaling and a examinations and prompt removal of basal cell skin abnormal hedgehog signaling pathway; such studies
dramatically increased risk of cancer. Patients with cancers help decrease the size of scarring and disfigure- may lead to medical options for these patients in the
BCNS are more sensitive to damage from ultraviolet ment resulting from surgery. All patients need to be future. Jaw cysts are best removed surgically to relieve
light and radiation than normal controls. educated at an early age on avoiding excessive sun expo- pain and discomfort. Medulloblastoma is a serious,
Histology: BCC in the BCNS syndrome is histologi- sure, tanning, and unnecessary radiation exposure from life-threatening tumor most commonly seen in early
cally the same as any other BCC, and there are no medical testing, because all of these increase the likeli- childhood, before the age of 4 years. Surgical and
distinguishing factors. hood of BCC development. Many ongoing research chemotherapeutic options exist.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 229