Page 245 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 245
Plate 9-5 Genodermatoses and Syndromes
CLINICAL FINDINGS OF CUSHING’S SYNDROME
CUSHING’S SYNDROME
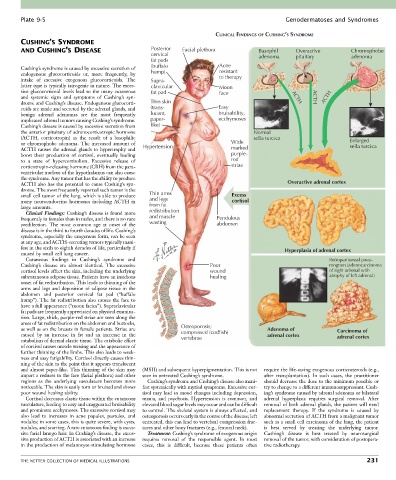
AND CUSHING’S DISEASE Posterior Facial plethora Basophil Overactive Chromophobe
cervical adenoma pituitary adenoma
fat pads
Cushing’s syndrome is caused by excessive secretion of (buffalo Acne
endogenous glucocorticoids or, more frequently, by hump) resistant
intake of excessive exogenous glucocorticoids. The Supra- to therapy
latter type is typically iatrogenic in nature. The exces- clavicular Moon
sive glucocorticoid levels lead to the many cutaneous fat pad face
and systemic signs and symptoms of Cushing’s syn- ACTH ACTH ACTH
drome and Cushing’s disease. Endogenous glucocorti- Thin skin
coids are made and secreted by the adrenal glands, and (trans- Easy
benign adrenal adenomas are the most frequently lucent, bruisability,
implicated adrenal tumors causing Cushing’s syndrome. paper- ecchymoses
Cushing’s disease is caused by excessive secretion from like)
the anterior pituitary of adrenocorticotropic hormone Normal
(ACTH, corticotropin) as the result of a basophilic sella turcica Enlarged
or chromophobe adenoma. The increased amount of Hypertension Wide sella turcica
ACTH causes the adrenal glands to hypertrophy and marked
boost their production of cortisol, eventually leading purple-
to a state of hypercortisolism. Excessive release of red
corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) from the para- striae
ventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus can also cause
the syndrome. Any tumor that has the ability to produce
ACTH also has the potential to cause Cushing’s syn- Overactive adrenal cortex
drome. The most frequently reported such tumor is the
small cell tumor of the lung, which is able to produce Thin arms Excess
many neuroendocrine hormones including ACTH in and legs cortisol
large amounts. from fat
Clinical Findings: Cushing’s disease is found more redistribution
frequently in females than in males, and there is no race and muscle Pendulous
predilection. The most common age at onset of the wasting abdomen
disease is in the third to fourth decades of life. Cushing’s
syndrome, especially the exogenous form, can be seen
at any age, and ACTH-secreting tumors typically mani-
fest in the sixth to eighth decades of life, particularly if Hyperplasia of adrenal cortex
caused by small cell lung cancer.
Cutaneous findings in Cushing’s syndrome and Retroperitoneal pneu-
Cushing’s disease are almost identical. The excessive Poor mogram (adenocarcinoma
cortisol levels affect the skin, including the underlying wound of right adrenal with
subcutaneous adipose tissue. Patients have an insidious healing atrophy of left adrenal)
onset of fat redistribution. This leads to thinning of the
arms and legs and deposition of adipose tissue in the
abdomen and posterior cervical fat pad (“buffalo
hump”). The fat redistribution also causes the face to
have a full appearance (“moon facies”). Supraclavicular
fat pads are frequently appreciated on physical examina-
tion. Large, thick, purple-red striae are seen along the
areas of fat redistribution on the abdomen and buttocks,
as well as on the breasts in female patients. Striae are Osteoporosis; Adenoma of Carcinoma of
caused by an increase in fat and an increase in the compressed (codfish) adrenal cortex adrenal cortex
catabolism of dermal elastic tissue. The catabolic effect vertebrae
of cortisol causes muscle wasting and the appearance of
further thinning of the limbs. This also leads to weak-
ness and easy fatigability. Cortisol directly causes thin-
ning of the skin to the point that it appears translucent
and almost paper-like. This thinning of the skin may (MSH) and subsequent hyperpigmentation. This is not require the life-saving exogenous corticosteroids (e.g.,
impart a redness to the face (facial plethora) and other seen in untreated Cushing’s syndrome. after transplantation). In such cases, the practitioner
regions as the underlying vasculature becomes more Cushing’s syndrome and Cushing’s disease also mani- should decrease the dose to the minimum possible or
noticeable. The skin is easily torn or bruised and shows fest systemically with myriad symptoms. Excessive cor- try to change to a different immunosuppressant. Cush-
poor wound healing ability. tisol may lead to mood changes including depression, ing’s syndrome caused by adrenal adenoma or bilateral
Cortisol decreases elastic tissue within the cutaneous mania, and psychosis. Hypertension is common, and adrenal hyperplasia requires surgical removal. After
vasculature, leading to easy and exaggerated bruisability elevated blood sugar levels may occur and can be difficult removal of both adrenal glands, the patient will need
and prominent ecchymoses. The excessive cortisol may to control. The skeletal system is always affected, and replacement therapy. If the syndrome is caused by
also lead to increases in acne papules, pustules, and osteoporosis occurs early in the course of the disease; left abnormal secretion of ACTH from a malignant tumor
nodules; in some cases, this is quite severe, with cysts, untreated, this can lead to vertebral compression frac- such as a small cell carcinoma of the lung, the patient
nodules, and scarring. A rare cutaneous finding is exces- tures and other bony fractures (e.g., femoral neck). is best served by treating the underlying tumor.
sive facial lanugo hair. In Cushing’s disease, the exces- Treatment: Cushing’s syndrome of exogenous origin Cushing’s disease is best treated by neurosurgical
sive production of ACTH is associated with an increase requires removal of the responsible agent. In most removal of the tumor, with consideration of postopera-
in the production of melanocyte-stimulating hormone cases, this is difficult, because these patients often tive radiotherapy.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 231