Page 67 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 67
Plate 3-2 Malignant Growths
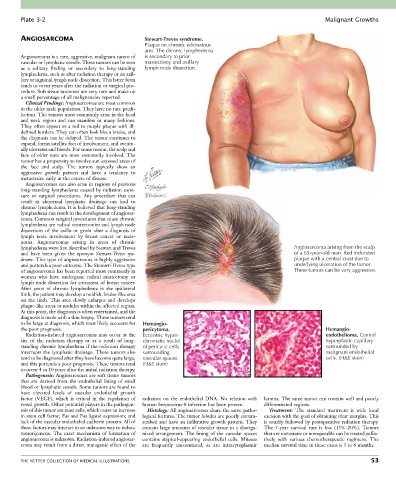
ANGIOSARCOMA Stewart-Treves syndrome.
Plaque on chronic edematous
arm. The chronic lymphedema
Angiosarcoma is a rare, aggressive, malignant tumor of is secondary to prior
vascular or lymphatic vessels. These tumors can be seen mastectomy and axillary
as a solitary finding or secondary to long-standing lymph node dissection.
lymphedema, such as after radiation therapy or an axil-
lary or inguinal lymph node dissection. This latter form
tends to occur years after the radiation or surgical pro-
cedure. Soft tissue sarcomas are very rare and make up
a small percentage of all malignancies reported.
Clinical Findings: Angiosarcomas are most common
in the older male population. They have no race predi-
lection. The tumors most commonly arise in the head
and neck region and can manifest in many fashions.
They often appear as a red to purple plaque with ill-
defined borders. They can often look like a bruise, and
the diagnosis can be delayed. The tumor continues to
expand, forms satellite foci of involvement, and eventu-
ally ulcerates and bleeds. For some reason, the scalp and
face of older men are most commonly involved. The
tumor has a propensity to involve sun-exposed areas of
the face and scalp. The tumors typically show an
aggressive growth pattern and have a tendency to
metastasize early in the course of disease.
Angiosarcomas can also arise in regions of previous
long-standing lymphedema caused by radiation expo-
sure or surgical procedures. Any procedure that can
result in abnormal lymphatic drainage can lead to
chronic lymphedema. It is believed that long-standing
lymphedema can result in the development of angiosar-
coma. Common surgical procedures that cause chronic
lymphedema are radical mastectomies and lymph node
dissections of the axilla or groin after a diagnosis of
lymph node involvement by breast cancer or mela-
noma. Angiosarcomas arising in areas of chronic
lymphedema were first described by Stewart and Treves Angiosarcoma arising from the scalp
and have been given the eponym Stewart-Treves syn- of a 65-year-old man. Red indurated
drome. This type of angiosarcoma is highly aggressive plaque with a central crust due to
and portends a poor outcome. The Stewart-Treves type underlying ulceration of the tumor.
of angiosarcoma has been reported most commonly in These tumors can be very aggressive.
women who have undergone radical mastectomy or
lymph node dissection for treatment of breast cancer.
After years of chronic lymphedema in the ipsilateral
limb, the patient may develop a reddish, bruise-like area
on the limb. This area slowly enlarges and develops
plaque-like areas or nodules within the affected region.
At this point, the diagnosis is often entertained, and the
diagnosis is made with a skin biopsy. These tumors tend
to be large at diagnosis, which most likely accounts for Hemangio-
the poor prognosis. pericytoma. Hemangio-
Radiation-induced angiosarcomas may occur at the Eccentric hyper- endothelioma. Central
site of the radiation therapy or as a result of long- chromatic nuclei hyperplastic capillary
standing chronic lymphedema if the radiation therapy of pericytic cells surrounded by
interrupts the lymphatic drainage. These tumors also surrounding malignant endothelial
tend to be diagnosed after they have become quite large, vascular spaces. cells. (H&E stain)
and this portends a poor prognosis. These tumors tend (H&E stain)
to occur 4 to 10 years after the initial radiation therapy.
Pathogenesis: Angiosarcomas are soft tissue tumors
that are derived from the endothelial lining of small
blood or lymphatic vessels. Some tumors are found to
have elevated levels of vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF), which is critical in the regulation of radiation on the endothelial DNA. No relation with lumina. The same tumor can contain well and poorly
vessel growth. Other potential players in the pathogen- human herpesvirus-8 infection has been proven. differentiated regions.
esis of this tumor are mast cells, which cause an increase Histology: All angiosarcomas share the same patho- Treatment: The standard treatment is wide local
in stem cell factor; Fas and Fas ligand expression; and logical features. The tumor lobules are poorly circum- excision with the goal of obtaining clear margins. This
lack of the vascular endothelial cadherin protein. All of scribed and have an infiltrative growth pattern. They is usually followed by postoperative radiation therapy.
these factors may interact in an unknown way to induce contain large amounts of vascular tissue in a disorga- The 5-year survival rate is low (15%-20%). Tumors
tumorigenesis. The exact mechanism of formation of nized arrangement. The lining of the vascular spaces that are metastatic or nonoperable can be treated pallia-
angiosarcoma is unknown. Radiation-induced angiosar- contains atypical-appearing endothelial cells. Mitoses tively with various chemotherapeutic regimens. The
coma may result from a direct mutagenic effect of the are frequently encountered, as are intracytoplasmic median survival time in these cases is 3 to 6 months.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 53