Page 68 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 68
Plate 3-3 Integumentary System
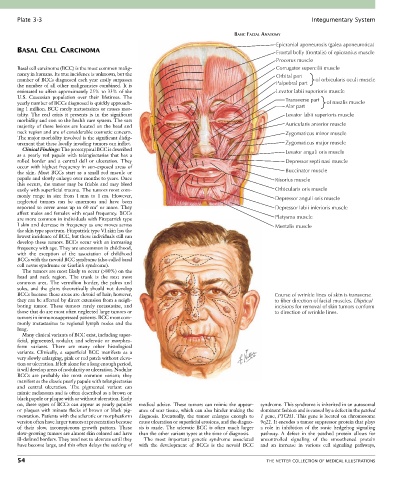
BASIC FACIAL ANATOMY
Epicranial aponeurosis (galea aponeurotica)
BASAL CELL CARCINOMA Frontal belly (frontalis) of epicranius muscle
Procerus muscle
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common malig- Corrugator supercilii muscle
nancy in humans. Its true incidence is unknown, but the Orbital part
number of BCCs diagnosed each year easily surpasses of orbicularis oculi muscle
the number of all other malignancies combined. It is Palpebral part
estimated to affect approximately 25% to 33% of the Levator labii superioris muscle
U.S. Caucasian population over their lifetimes. The Transverse part
yearly number of BCCs diagnosed is quickly approach- of nasalis muscle
ing 1 million. BCC rarely metastasizes or causes mor- Alar part
tality. The real crisis it presents is in the significant Levator labii superioris muscle
morbidity and cost to the health care system. The vast
majority of these lesions are located on the head and Auricularis anterior muscle
neck region and are of considerable cosmetic concern. Zygomaticus minor muscle
The major morbidity involved is the significant disfig-
urement that these locally invading tumors can inflict. Zygomaticus major muscle
Clinical Findings: The prototypical BCC is described
as a pearly red papule with telangiectasias that has a Levator anguli oris muscle
rolled border and a central dell or ulceration. They Depressor septi nasi muscle
occur with highest frequency in sun-exposed areas of
the skin. Most BCCs start as a small red macule or Buccinator muscle
papule and slowly enlarge over months to years. Once Risorius muscle
this occurs, the tumor may be friable and may bleed
easily with superficial trauma. The tumors most com- Orbicularis oris muscle
monly range in size from 1 mm to 1 cm. However, Depressor anguli oris muscle
neglected tumors can be enormous and have been
reported to cover areas up to 60 cm or more. They Depressor labii inferioris muscle
2
affect males and females with equal frequency. BCCs
are more common in individuals with Fitzpatrick type Platysma muscle
I skin and decrease in frequency as one moves across Mentalis muscle
the skin type spectrum. Fitzpatrick type VI skin has the
lowest incidence of BCC, but these individuals still can
develop these tumors. BCCs occur with an increasing
frequency with age. They are uncommon in childhood,
with the exception of the association of childhood
BCCs with the nevoid BCC syndrome (also called basal
cell nevus syndrome or Gorlin’s syndrome).
The tumors are most likely to occur (>80%) on the
head and neck region. The trunk is the next most
common area. The vermilion border, the palms and
soles, and the glans theoretically should not develop
BCCs because these areas are devoid of hair; however, Course of wrinkle lines of skin is transverse
they can be affected by direct extension from a neigh- to fiber direction of facial muscles. Elliptical
boring tumor. These tumors rarely metastasize, and incisions for removal of skin tumors conform
those that do are most often neglected large tumors or to direction of wrinkle lines.
tumors in immunosuppressed patients. BCC most com-
monly metastasizes to regional lymph nodes and the
lung.
Many clinical variants of BCC exist, including super-
ficial, pigmented, nodular, and sclerotic or morphea-
form variants. There are many other histological
variants. Clinically, a superficial BCC manifests as a
very slowly enlarging, pink or red patch without eleva-
tion or ulceration. If left alone for a long enough period,
it will develop areas of nodularity or ulceration. Nodular
BCCs are probably the most common variant; they
manifest as the classic pearly papule with telangiectasias
and central ulceration. The pigmented variant can
mimic melanoma and is often described as a brown or
black papule or plaque with or without ulceration. Early
on, these types of BCCs can appear as pearly papules medical advice. These tumors can mimic the appear- syndrome. This syndrome is inherited in an autosomal
or plaques with minute flecks of brown or black pig- ance of scar tissue, which can also hinder making the dominant fashion and is caused by a defect in the patched
mentation. Patients with the sclerotic or morpheaform diagnosis. Eventually, the tumor enlarges enough to 1 gene, PTCH1. This gene is located on chromosome
version often have larger tumors at presentation because cause ulceration or superficial erosions, and the diagno- 9q22. It encodes a tumor suppressor protein that plays
of their slow, inconspicuous growth pattern. These sis is made. The sclerotic BCC is often much larger a role in inhibition of the sonic hedgehog signaling
slow-growing tumors are almost skin colored and have than the other variant types at the time of diagnosis. pathway. A defect in the patched protein allows for
ill-defined borders. They tend not to ulcerate until they The most important genetic syndrome associated uncontrolled signaling of the smoothened protein
have become large, and this often delays the seeking of with the development of BCCs is the nevoid BCC and an increase in various cell signaling pathways,
54 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS