Page 69 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 69
Plate 3-4 Malignant Growths
CLINICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF BASAL CELL CARCINOMA
BASAL CELL CARCINOMA
(Continued)
ultimately culminating in the development of BCCs.
Patients with nevoid BCC syndrome also may have
odontogenic cysts of the jaw, palmar and plantar pitting,
various bony abnormalities, and calcification of the falx
cerebri. Frontal bossing, mental delay, and ovarian
fibromas are only a few of the associated findings that
can be seen in this syndrome.
Other rare syndromes in which BCCs can be seen
include xeroderma pigmentosa, Bazek’s syndrome, and
Rombo syndrome.
Pathogenesis: Risk factors associated with the devel-
opment of BCC include cumulative exposure to ultra-
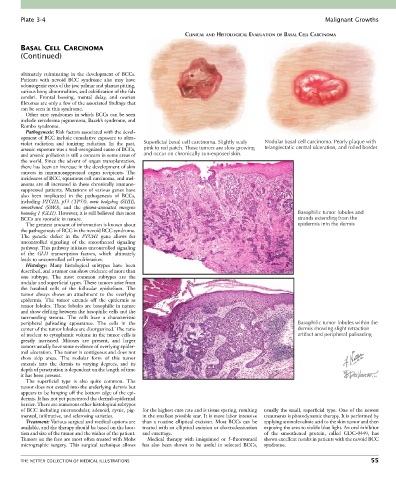
violet radiation and ionizing radiation. In the past, Superficial basal cell carcinoma. Slightly scaly Nodular basal cell carcinoma. Pearly plaque with
arsenic exposure was a well-recognized cause of BCCs, pink to red patch. These tumors are slow growing telangiectatic central ulceration, and rolled border
and arsenic pollution is still a concern in some areas of and occur on chronically sun-exposed skin.
the world. Since the advent of organ transplantation,
there has been an increase in the development of skin
cancers in immunosuppressed organ recipients. The
incidences of BCC, squamous cell carcinoma, and mel-
anoma are all increased in these chronically immuno-
suppressed patients. Mutations of various genes have
also been implicated in the pathogenesis of BCCs,
including PTCH1, p53 ( TP53), sonic hedgehog (SHH),
smoothened (SMO), and the glioma-associated oncogene
homolog 1 (GLI1). However, it is still believed that most Basophilic tumor lobules and
BCCs are sporadic in nature. strands extending from the
The greatest amount of information is known about epidermis into the dermis
the pathogenesis of BCC in the nevoid BCC syndrome.
The genetic defect in the PTCH1 gene allows for
uncontrolled signaling of the smoothened signaling
pathway. This pathway initiates uncontrolled signaling
of the GLI1 transcription factors, which ultimately
leads to uncontrolled cell proliferation.
Histology: Many histological subtypes have been
described, and a tumor can show evidence of more than
one subtype. The most common subtypes are the
nodular and superficial types. These tumors arise from
the basaloid cells of the follicular epithelium. The
tumor always shows an attachment to the overlying
epidermis. The tumor extends off the epidermis as
tumor lobules. These lobules are basophilic in nature
and show clefting between the basophilic cells and the
surrounding stroma. The cells have a characteristic
peripheral palisading appearance. The cells in the Basophilic tumor lobules within the
center of the tumor lobules are disorganized. The ratio dermis showing slight retraction
of nuclear to cytoplasmic volume in the tumor cells is artifact and peripheral palisading
greatly increased. Mitoses are present, and larger
tumors usually have some evidence of overlying epider-
mal ulceration. The tumor is contiguous and does not
show skip areas. The nodular form of this tumor
extends into the dermis to varying degrees, and its
depth of penetration is dependent on the length of time
it has been present.
The superficial type is also quite common. The
tumor does not extend into the underlying dermis but
appears to be hanging off the bottom edge of the epi-
dermis. It has not yet penetrated the dermal-epidermal
barrier. There are numerous other histological subtypes
of BCC including micronodular, adenoid, cystic, pig- for the highest cure rate and is tissue sparing, resulting usually the small, superficial type. One of the newest
mented, infiltrative, and sclerosing varieties. in the smallest possible scar. It is more labor intensive treatments is photodynamic therapy. It is performed by
Treatment: Various surgical and medical options are than a routine elliptical excision. Most BCCs can be applying aminolevulinic acid to the skin tumor and then
available, and the therapy should be based on the loca- treated with an elliptical excision or electrodessication exposing the area to visible blue light. An oral inhibitor
tion and size of the tumor and the wishes of the patient. and curettage. of the smoothened protein, called GDC-0449, has
Tumors on the face are most often treated with Mohs Medical therapy with imiquimod or 5-fluorouracil shown excellent results in patients with the nevoid BCC
micrographic surgery. This surgical technique allows has also been shown to be useful in selected BCCs, syndrome.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 55