Page 207 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 207
Airway Management in Mechanical Ventilation 173
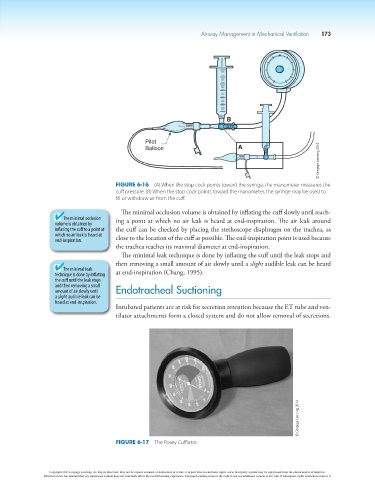
B
O F F
Pilot
© Cengage Learning 2014
Balloon A
O F F
Figure 6-16 (A) When the stop cock points toward the syringe, the manometer measures the
cuff pressure. (B) When the stop cock points toward the manometer, the syringe may be used to
fill or withdraw air from the cuff.
The minimal occlusion volume is obtained by inflating the cuff slowly until reach-
The minimal occlusion ing a point at which no air leak is heard at end-inspiration. The air leak around
volume is obtained by
inflating the cuff to a point at the cuff can be checked by placing the stethoscope diaphragm on the trachea, as
which no air leak is heard at close to the location of the cuff as possible. The end-inspiration point is used because
end-inspiration.
the trachea reaches its maximal diameter at end-inspiration.
The minimal leak technique is done by inflating the cuff until the leak stops and
then removing a small amount of air slowly until a slight audible leak can be heard
The minimal leak at end-inspiration (Chang, 1995).
technique is done by inflating
the cuff until the leak stops
and then removing a small
amount of air slowly until Endotracheal Suctioning
a slight audible leak can be
heard at end-inspiration.
Intubated patients are at risk for secretion retention because the ET tube and ven-
tilator attachments form a closed system and do not allow removal of secretions.
© Cengage Learning 2014
Figure 6-17 The Posey Cufflator.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.