Page 322 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 322
288 Chapter 10
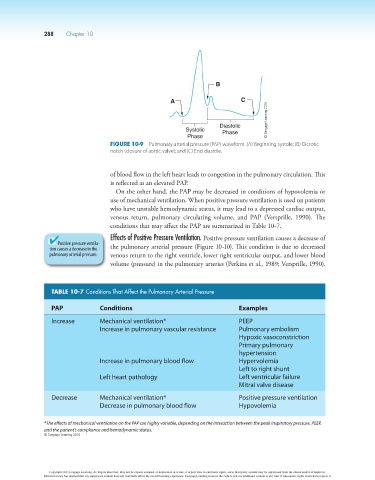
B
A C
© Cengage Learning 2014
Diastolic
Systolic Phase
Phase
Figure 10-9 Pulmonary arterial pressure (PAP) waveform. (A) Beginning systole; (B) Dicrotic
notch (closure of aortic valve); and (C) End diastole.
of blood flow in the left heart leads to congestion in the pulmonary circulation. This
is reflected as an elevated PAP.
On the other hand, the PAP may be decreased in conditions of hypovolemia or
use of mechanical ventilation. When positive pressure ventilation is used on patients
who have unstable hemodynamic status, it may lead to a depressed cardiac output,
venous return, pulmonary circulating volume, and PAP (Versprille, 1990). The
conditions that may affect the PAP are summarized in Table 10-7.
Effects of Positive Pressure Ventilation. Positive pressure ventilation causes a decrease of
Positive pressure ventila-
tion causes a decrease in the the pulmonary arterial pressure (Figure 10-10). This condition is due to decreased
pulmonary arterial pressure. venous return to the right ventricle, lower right ventricular output, and lower blood
volume (pressure) in the pulmonary arteries (Perkins et al., 1989; Versprille, 1990).
TABLE 10-7 Conditions That Affect the Pulmonary Arterial Pressure
PAP Conditions Examples
Increase Mechanical ventilation* PEEP
Increase in pulmonary vascular resistance Pulmonary embolism
Hypoxic vasoconstriction
Primary pulmonary
hypertension
Increase in pulmonary blood flow Hypervolemia
Left to right shunt
Left heart pathology Left ventricular failure
Mitral valve disease
Decrease Mechanical ventilation* Positive pressure ventilation
Decrease in pulmonary blood flow Hypovolemia
*The effects of mechanical ventilation on the PAP are highly variable, depending on the interaction between the peak inspiratory pressure, PEEP,
and the patient’s compliance and hemodynamic status.
© Cengage Learning 2014
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.