Page 321 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 321
Hemodynamic Monitoring 287
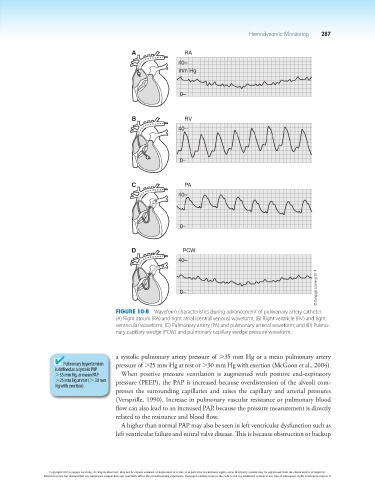
A RA
40–
mm Hg
0–
B RV
40–
0–
C PA
40–
0–
D PCW
40–
© Cengage Learning 2014
0–
Figure 10-8 Waveform characteristics during advancement of pulmonary artery catheter.
(A) Right atrium (RA) and right atrial (central venous) waveform; (B) Right ventricle (RV) and right
ventricular waveform; (C) Pulmonary artery (PA) and pulmonary arterial waveform; and (D) Pulmo-
nary capillary wedge (PCW) and pulmonary capillary wedge pressure waveform.
a systolic pulmonary artery pressure of .35 mm Hg or a mean pulmonary artery
Pulmonary hypertension pressure of .25 mm Hg at rest or .30 mm Hg with exertion (McGoon et al., 2004).
is defined as a systolic PAP
.35 mm Hg, or mean PAP When positive pressure ventilation is augmented with positive end-expiratory
.25 mm Hg at rest (. 30 mm pressure (PEEP), the PAP is increased because overdistension of the alveoli com-
Hg with exertion).
presses the surrounding capillaries and raises the capillary and arterial pressures
(Versprille, 1990). Increase in pulmonary vascular resistance or pulmonary blood
flow can also lead to an increased PAP, because the pressure measurement is directly
related to the resistance and blood flow.
A higher than normal PAP may also be seen in left ventricular dysfunction such as
left ventricular failure and mitral valve disease. This is because obstruction or backup
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.