Page 320 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 320
286 Chapter 10
© Cengage Learning 2014
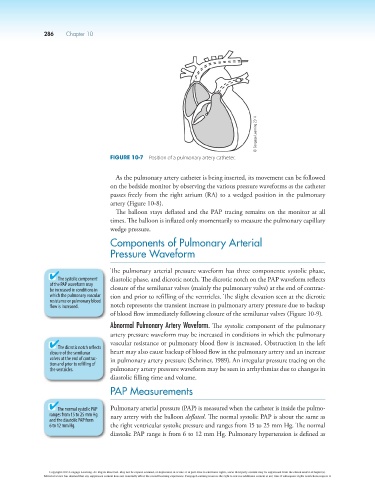
Figure 10-7 Position of a pulmonary artery catheter.
As the pulmonary artery catheter is being inserted, its movement can be followed
on the bedside monitor by observing the various pressure waveforms as the catheter
passes freely from the right atrium (RA) to a wedged position in the pulmonary
artery (Figure 10-8).
The balloon stays deflated and the PAP tracing remains on the monitor at all
times. The balloon is inflated only momentarily to measure the pulmonary capillary
wedge pressure.
Components of Pulmonary Arterial
Pressure Waveform
The pulmonary arterial pressure waveform has three components: systolic phase,
The systolic component diastolic phase, and dicrotic notch. The dicrotic notch on the PAP waveform reflects
of the PAP waveform may
be increased in conditions in closure of the semilunar valves (mainly the pulmonary valve) at the end of contrac-
which the pulmonary vascular tion and prior to refilling of the ventricles. The slight elevation seen at the dicrotic
resistance or pulmonary blood
flow is increased. notch represents the transient increase in pulmonary artery pressure due to backup
of blood flow immediately following closure of the semilunar valves (Figure 10-9).
Abnormal Pulmonary Artery Waveform. The systolic component of the pulmonary
artery pressure waveform may be increased in conditions in which the pulmonary
vascular resistance or pulmonary blood flow is increased. Obstruction in the left
The dicrotic notch reflects
closure of the semilunar heart may also cause backup of blood flow in the pulmonary artery and an increase
valves at the end of contrac- in pulmonary artery pressure (Schriner, 1989). An irregular pressure tracing on the
tion and prior to refilling of
the ventricles. pulmonary artery pressure waveform may be seen in arrhythmias due to changes in
diastolic filling time and volume.
PAP Measurements
The normal systolic PAP Pulmonary arterial pressure (PAP) is measured when the catheter is inside the pulmo-
ranges from 15 to 25 mm Hg nary artery with the balloon deflated. The normal systolic PAP is about the same as
and the diastolic PAP from
6 to 12 mm Hg. the right ventricular systolic pressure and ranges from 15 to 25 mm Hg. The normal
diastolic PAP range is from 6 to 12 mm Hg. Pulmonary hypertension is defined as
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.