Page 434 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 434
400 Chapter 12
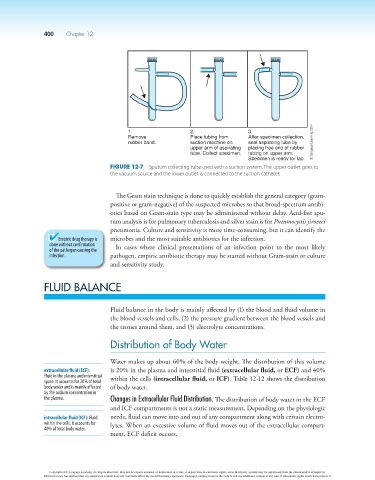
1. 2. 3.
Remove Place tubing from After specimen collection,
rubber band. suction machine on seal aspirating tube by © Cengage Learning 2014
upper arm of aspirating placing free end of rubber
tube. Collect specimen. tubing on upper arm.
Specimen is ready for lab.
Figure 12-7 Sputum collecting tube used with a suction system. The upper outlet goes to
the vacuum source and the lower outlet is connected to the suction catheter.
The Gram stain technique is done to quickly establish the general category (gram-
positive or gram-negative) of the suspected microbes so that broad-spectrum antibi-
otics based on Gram-stain type may be administered without delay. Acid-fast spu-
tum analysis is for pulmonary tuberculosis and silver stain is for Pneumocystis jiroveci
pneumonia. Culture and sensitivity is more time-consuming, but it can identify the
Empiric drug therapy is microbes and the most suitable antibiotics for the infection.
done without confirmation In cases where clinical presentations of an infection point to the most likely
of the pathogen causing the
infection. pathogen, empiric antibiotic therapy may be started without Gram-stain or culture
and sensitivity study.
FLUID BALANCE
Fluid balance in the body is mainly affected by (1) the blood and fluid volume in
the blood vessels and cells, (2) the pressure gradient between the blood vessels and
the tissues around them, and (3) electrolyte concentrations.
Distribution of Body Water
Water makes up about 60% of the body weight. The distribution of this volume
extracellular fluid (ECF): is 20% in the plasma and interstitial fluid (extracellular fluid, or ECF) and 40%
Fluid in the plasma and interstitial within the cells (intracellular fluid, or ICF). Table 12-12 shows the distribution
space. It accounts for 20% of total
body water and is mainly affected of body water.
by the sodium concentration in
the plasma. Changes in Extracellular Fluid Distribution. The distribution of body water in the ECF
and ICF compartments is not a static measurement. Depending on the physiologic
intracellular fluid (ICF): Fluid needs, fluid can move into and out of any compartment along with certain electro-
within the cells. It accounts for lytes. When an excessive volume of fluid moves out of the extracellular compart-
40% of total body water.
ment, ECF deficit occurs.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.