Page 437 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 437
Management of Mechanical Ventilation 403
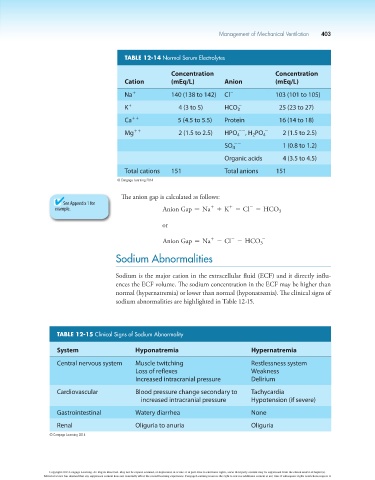
TABLE 12-14 Normal Serum Electrolytes
Concentration Concentration
Cation (mEq/L) Anion (mEq/L)
Na 1 140 (138 to 142) Cl 2 103 (101 to 105)
K 1 4 (3 to 5) HCO - 25 (23 to 27)
3
Ca 11 5 (4.5 to 5.5) Protein 16 (14 to 18)
Mg 11 2 (1.5 to 2.5) HPO - - , H PO - 2 (1.5 to 2.5)
4
4
2
SO - - 1 (0.8 to 1.2)
4
Organic acids 4 (3.5 to 4.5)
Total cations 151 Total anions 151
© Cengage Learning 2014
The anion gap is calculated as follows:
See Appendix 1 for
example. Anion Gap = Na + + K + - Cl - - HCO 3 -
or
-
Anion Gap = Na + - Cl - - HCO
3
Sodium Abnormalities
Sodium is the major cation in the extracellular fluid (ECF) and it directly influ-
ences the ECF volume. The sodium concentration in the ECF may be higher than
normal (hypernatremia) or lower than normal (hyponatremia). The clinical signs of
sodium abnormalities are highlighted in Table 12-15.
TABLE 12-15 Clinical Signs of Sodium Abnormality
System Hyponatremia Hypernatremia
Central nervous system Muscle twitching Restlessness system
Loss of reflexes Weakness
Increased intracranial pressure Delirium
Cardiovascular Blood pressure change secondary to Tachycardia
increased intracranial pressure Hypotension (if severe)
Gastrointestinal Watery diarrhea None
Renal Oliguria to anuria Oliguria
© Cengage Learning 2014
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.