Page 435 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 435
Management of Mechanical Ventilation 401
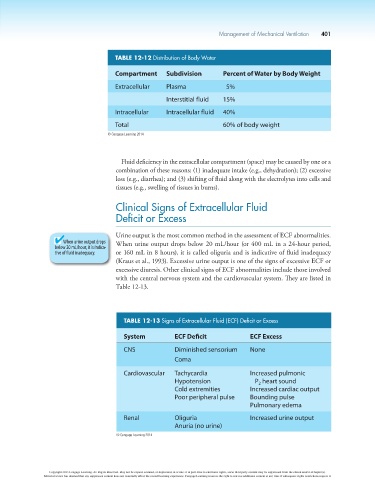
TABLE 12-12 Distribution of Body Water
Compartment Subdivision Percent of Water by Body Weight
Extracellular Plasma 5%
Interstitial fluid 15%
Intracellular Intracellular fluid 40%
Total 60% of body weight
© Cengage Learning 2014
Fluid deficiency in the extracellular compartment (space) may be caused by one or a
combination of these reasons: (1) inadequate intake (e.g., dehydration); (2) excessive
loss (e.g., diarrhea); and (3) shifting of fluid along with the electrolytes into cells and
tissues (e.g., swelling of tissues in burns).
Clinical Signs of Extracellular Fluid
Deficit or Excess
Urine output is the most common method in the assessment of ECF abnormalities.
When urine output drops When urine output drops below 20 mL/hour (or 400 mL in a 24-hour period,
below 20 mL/hour, it is indica-
tive of fluid inadequacy. or 160 mL in 8 hours), it is called oliguria and is indicative of fluid inadequacy
(Kraus et al., 1993). Excessive urine output is one of the signs of excessive ECF or
excessive diuresis. Other clinical signs of ECF abnormalities include those involved
with the central nervous system and the cardiovascular system. They are listed in
Table 12-13.
TABLE 12-13 Signs of Extracellular Fluid (ECF) Deficit or Excess
System ECF Deficit ECF Excess
CNS Diminished sensorium None
Coma
Cardiovascular Tachycardia Increased pulmonic
Hypotension P heart sound
2
Cold extremities Increased cardiac output
Poor peripheral pulse Bounding pulse
Pulmonary edema
Renal Oliguria Increased urine output
Anuria (no urine)
© Cengage Learning 2014
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.