Page 65 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 65
Effects of Positive Pressure Ventilation 31
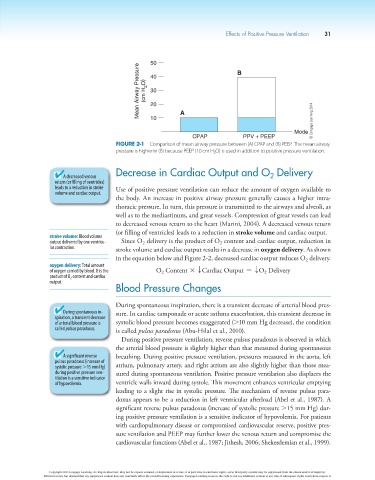
50 B
Mean Airway Pressure (cm H 2 O) 30
40
20
A
10
Mode © Cengage Learning 2014
CPAP PPV + PEEP
Figure 2-1 Comparison of mean airway pressure between (A) CPAP and (B) PEEP. The mean airway
pressure is higher in (B) because PEEP (10 cm H 2 O) is used in addition to positive pressure ventilation.
Decrease in Cardiac Output and O Delivery
A decreased venous 2
return (or filling of ventricles)
leads to a reduction in stroke Use of positive pressure ventilation can reduce the amount of oxygen available to
volume and cardiac output.
the body. An increase in positive airway pressure generally causes a higher intra-
thoracic pressure. In turn, this pressure is transmitted to the airways and alveoli, as
well as to the mediastinum, and great vessels. Compression of great vessels can lead
to decreased venous return to the heart (Marini, 2004). A decreased venous return
(or filling of ventricles) leads to a reduction in stroke volume and cardiac output.
stroke volume: Blood volume
output delivered by one ventricu- Since O delivery is the product of O content and cardiac output, reduction in
2
2
lar contraction. stroke volume and cardiac output results in a decrease in oxygen delivery. As shown
in the equation below and Figure 2-2, decreased cardiac output reduces O delivery.
2
oxygen delivery: Total amount
of oxygen carried by blood. It is the O Content * TCardiac Output = TO Delivery
2
2
product of O 2 content and cardiac
output.
Blood Pressure Changes
During spontaneous inspiration, there is a transient decrease of arterial blood pres-
During spontaneous in- sure. In cardiac tamponade or acute asthma exacerbation, this transient decrease in
spiration, a transient decrease
of arterial blood pressure is systolic blood pressure becomes exaggerated (.10 mm Hg decrease), the condition
called pulsus paradoxus. is called pulsus paradoxus (Abu-Hilal et al., 2010).
During positive pressure ventilation, reverse pulsus paradoxus is observed in which
the arterial blood pressure is slightly higher than that measured during spontaneous
A significant reverse breathing. During positive pressure ventilation, pressures measured in the aorta, left
pulsus paradoxus (increase of
systolic pressure .15 mm Hg) atrium, pulmonary artery, and right atrium are also slightly higher than those mea-
during positive pressure ven- sured during spontaneous ventilation. Positive pressure ventilation also displaces the
tilation is a sensitive indicator
of hypovolemia. ventricle walls inward during systole. This movement enhances ventricular emptying
leading to a slight rise in systolic pressure. The mechanism of reverse pulsus para-
doxus appears to be a reduction in left ventricular afterload (Abel et al., 1987). A
significant reverse pulsus paradoxus (increase of systolic pressure .15 mm Hg) dur-
ing positive pressure ventilation is a sensitive indicator of hypovolemia. For patients
with cardiopulmonary disease or compromised cardiovascular reserve, positive pres-
sure ventilation and PEEP may further lower the venous return and compromise the
cardiovascular functions (Abel et al., 1987; Jithesh, 2006; Shekerdemian et al., 1999).
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.