Page 70 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 70
36 Chapter 2
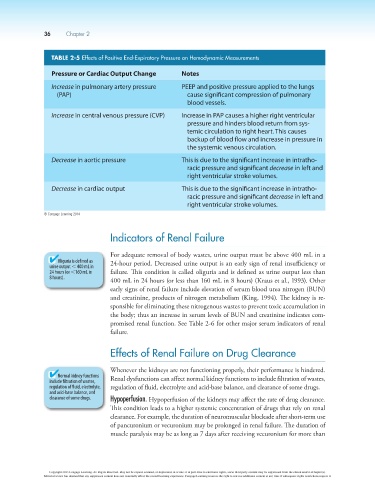
TABLE 2-5 Effects of Positive End-Expiratory Pressure on Hemodynamic Measurements
Pressure or Cardiac Output Change Notes
Increase in pulmonary artery pressure PEEP and positive pressure applied to the lungs
(PAP) cause significant compression of pulmonary
blood vessels.
Increase in central venous pressure (CVP) Increase in PAP causes a higher right ventricular
pressure and hinders blood return from sys-
temic circulation to right heart. This causes
backup of blood flow and increase in pressure in
the systemic venous circulation.
Decrease in aortic pressure This is due to the significant increase in intratho-
racic pressure and significant decrease in left and
right ventricular stroke volumes.
Decrease in cardiac output This is due to the significant increase in intratho-
racic pressure and significant decrease in left and
right ventricular stroke volumes.
© Cengage Learning 2014
Indicators of Renal Failure
For adequate removal of body wastes, urine output must be above 400 mL in a
Oliguria is defined as 24-hour period. Decreased urine output is an early sign of renal insufficiency or
urine output , 400 mL in
24 hours (or ,160 mL in failure. This condition is called oliguria and is defined as urine output less than
8 hours).
400 mL in 24 hours (or less than 160 mL in 8 hours) (Kraus et al., 1993). Other
early signs of renal failure include elevation of serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
and creatinine, products of nitrogen metabolism (King, 1994). The kidney is re-
sponsible for eliminating these nitrogenous wastes to prevent toxic accumulation in
the body; thus an increase in serum levels of BUN and creatinine indicates com-
promised renal function. See Table 2-6 for other major serum indicators of renal
failure.
Effects of Renal Failure on Drug Clearance
Whenever the kidneys are not functioning properly, their performance is hindered.
Normal kidney functions Renal dysfunctions can affect normal kidney functions to include filtration of wastes,
include filtration of wastes,
regulation of fluid, electrolyte, regulation of fluid, electrolyte and acid-base balance, and clearance of some drugs.
and acid-base balance, and
clearance of some drugs. Hypoperfusion. Hypoperfusion of the kidneys may affect the rate of drug clearance.
This condition leads to a higher systemic concentration of drugs that rely on renal
clearance. For example, the duration of neuromuscular blockade after short-term use
of pancuronium or vecuronium may be prolonged in renal failure. The duration of
muscle paralysis may be as long as 7 days after receiving vecuronium for more than
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.