Page 66 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 66
32 Chapter 2
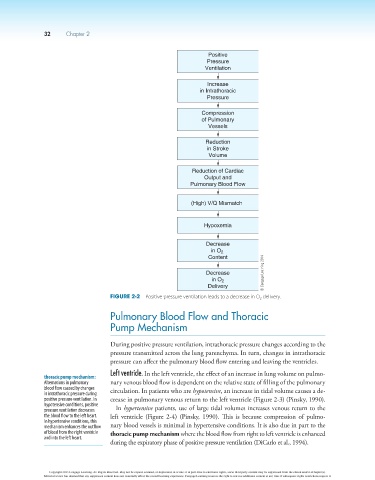
Positive
Pressure
Ventilation
Increase
in Intrathoracic
Pressure
Compression
of Pulmonary
Vessels
Reduction
in Stroke
Volume
Reduction of Cardiac
Output and
Pulmonary Blood Flow
(High) V/Q Mismatch
Hypoxemia
Decrease
in O
2
Content
Decrease © Cengage Learning 2014
in O 2
Delivery
Figure 2-2 Positive pressure ventilation leads to a decrease in O 2 delivery.
Pulmonary Blood Flow and Thoracic
Pump Mechanism
During positive pressure ventilation, intrathoracic pressure changes according to the
pressure transmitted across the lung parenchyma. In turn, changes in intrathoracic
pressure can affect the pulmonary blood flow entering and leaving the ventricles.
Left ventricle. In the left ventricle, the effect of an increase in lung volume on pulmo-
thoracic pump mechanism:
Alternations in pulmonary nary venous blood flow is dependent on the relative state of filling of the pulmonary
blood flow caused by changes circulation. In patients who are hypotensive, an increase in tidal volume causes a de-
in intrathoracic pressure during
positive pressure ventilation. In crease in pulmonary venous return to the left ventricle (Figure 2-3) (Pinsky, 1990).
hypotensive conditions, positive
pressure ventilation decreases In hypertensive patients, use of large tidal volumes increases venous return to the
the blood flow to the left heart. left ventricle (Figure 2-4) (Pinsky, 1990). This is because compression of pulmo-
In hypertensive conditions, this
mechanism enhances the outflow nary blood vessels is minimal in hypertensive conditions. It is also due in part to the
of blood from the right ventricle thoracic pump mechanism where the blood flow from right to left ventricle is enhanced
and into the left heart.
during the expiratory phase of positive pressure ventilation (DiCarlo et al., 1994).
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.