Page 182 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 182
LWBK340-c07_p153-176.qxd 6/29/09 10:14 PM Page 158 Aptara Inc.
158 PA R T II / Physiologic and Pathologic Responses
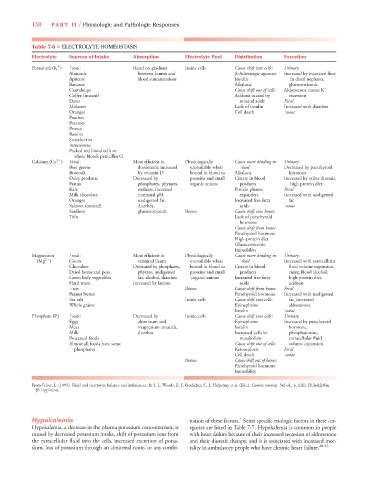
Table 7-6 ■ ELECTROLYTE HOMEOSTASIS
Electrolyte Sources of Intake Absorption Electrolyte Pool Distribution Excretion
Potassium (K ) Foods: Based on gradient Inside cells Cause shift into cells: Urinary:
Almonds between lumen and -Adrenergic agonists Increased by increased flow
Apricots blood concentrations Insulin in distal nephron,
Bananas Alkalosis glucocorticoids
Cantaloupe Cause shift out of cells: Aldosterone causes K
Coffee (instant) Acidosis caused by excretion
Dates mineral acids Fecal: l l
Molasses Lack of insulin Increased with diarrhea
Oranges Cell death Sweat
Peaches
Potatoes
Prunes
Raisins
Strawberries
Intravenous:
Packed red blood cells or
whole blood; penicillin G
2
Calcium (Ca ) Foods: Most efficient in Physiologically Cause more binding in Urinary:
Beet greens duodenum; increased unavailable when blood: Decreased by parathyroid
Broccoli by vitamin D bound in blood to Alkalosis hormone
Dairy products Decreased by proteins and small Citrate in blood Increased by saline diuresis,
Farina phosphates, phytates, organic anions products high protein diet
Kale oxalates, increased Protein plasma Fecal:
Milk chocolate intestinal pH, expanders Increased with undigested
Oranges undigested fat, Increased free fatty fat
Salmon (canned) diarrhea, acids Sweat
Sardines glucocorticoids Bones Cause shift into bones:
Tofu Lack of parathyroid
hormone
Cause shift from bones:
Parathyroid hormone
High-protein diet
Glucocorticoids
Immobility
Magnesium Foods: Most efficient in Physiologically Cause more binding in Urinary:
2
d
(Mg ) Cocoa terminal ileum unavailable when blood: Increased with extracellular
d
Chocolate Decreased by phosphates, bound in blood to Citrate in blood fluid volume expansion,
Dried beans and peas phytate, undigested proteins and small products rising blood alcohol,
Green leafy vegetables fat, alcohol, diarrhea organic anions Increased free fatty high-protein diet,
Hard water Increased by lactose acids acidosis
Nuts Bones Cause shift from bones: Fecal:
Peanut butter Parathyroid hormone Increased with undigested
Sea salt Inside cells Cause shift into cells: fat, increased
Whole grains Epinephrine aldosterone
Insulin Sweat
Phosphate (P i ) Foods: Decreased by Inside cells Cause shift into cells: Urinary:
Eggs aluminum and Epinephrine Increased by parathyroid
Meat magnesium antacids, Insulin hormone,
Milk diarrhea Increased cellular phosphatonins,
Processed foods metabolism extracellular fluid
Almost all foods have some Cause shift out of cells: volume expansion
phosphates Ketoacidosis Fecal
Cell death Sweat
Bones Cause shift out of bones:
Parathyroid hormone
Immobility
From Felver, L. (1995). Fluid and electrolyte balance and imbalances. In S. L. Woods, E. S. Froelicher, C. J. Halpenny et al. (Eds.), Cardiac nursing (3rd ed., p. 126). Philadelphia:
JB Lippincott.
1
Hypokalemia nation of these factors. Some specific etiologic factors in these cat-
Hypokalemia, a decrease in the plasma potassium concentration, is egories are listed in Table 7-7. Hypokalemia is common in people
caused by decreased potassium intake, shift of potassium ions from with heart failure because of their increased secretion of aldosterone
the extracellular fluid into the cells, increased excretion of potas- and their diuretic therapy, and it is associated with increased mor-
sium, loss of potassium through an abnormal route, or any combi- tality in ambulatory people who have chronic heart failure. 20,21