Page 243 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 243
0:4
6 A
1
0:4
M
Pa
6 A
M
1
0/0
0/0
3
3
009
009
6/2
6/2
p
p
A
p
ara
ara
t
t
A
g
g
Pa
g
19
19
e 2
e 2
xd
1-2
LWBK340-c10_
K34
LWB K34 0-c 10_ pp211-244.qxd 30/06/2009 10:46 AM Page 219 Aptara
LWB
1-2
21
21
p
0-c
10_
p
q
44.
q
xd
q
44.
C HAPTER 1 0 / History Taking and Physical Examination 219
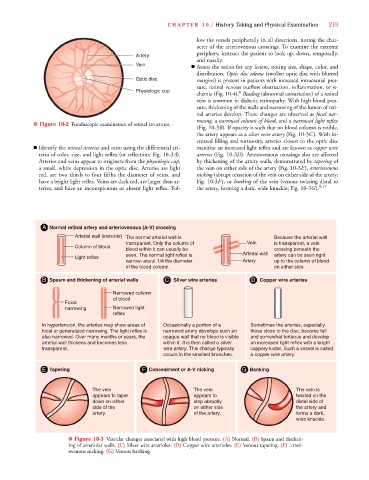
low the vessels peripherally in all directions, noting the char-
acter of the arteriovenous crossings. To examine the extreme
periphery, instruct the patient to look up, down, temporally,
Artery
and nasally.
Vein ■ Assess the retina for any lesions, noting size, shape, color, and
distribution. Optic disc edema (swollen optic disc with blurred
Optic disc margins) is present in patients with increased intracranial pres-
sure, retinal venous outflow obstruction, inflammation, or is-
Physiologic cup 8
chemia (Fig. 10-4). Beading (abnormal constriction) of a retinal
vein is common in diabetic retinopathy. With high blood pres-
sure, thickening of the walls and narrowing of the lumen of reti-
nal arteries develop. These changes are observed as focal nar-
rowing, a narrowed column of blood, and a narrowed light reflex
■ Figure 10-2 Funduscopic examination of retinal structures.
(Fig. 10-3B). If opacity is such that no blood column is visible,
B
the artery appears as a silver wire artery (Fig. 10-3C). With in-
creased filling and tortuosity, arteries closest to the optic disc
■ Identify the retinal arteries and veins using the differential cri- manifest an increased light reflex and are known as copper wire
teria of color, size, and light reflex (or reflection; Fig. 10-3A). arteries (Fig. 10-3D). Arteriovenous crossings also are affected
Arteries and veins appear to originate from the physiologic cup, by thickening of the artery walls, demonstrated by tapering of
a small, white depression in the optic disc. Arteries are light the vein on either side of the artery (Fig. 10-3E), arteriovenous
red, are two thirds to four fifths the diameter of veins, and nicking (abrupt cessation of the vein on either side of the artery;
have a bright light reflex. Veins are dark red, are larger than ar- Fig. 10-3F), or banking of the vein (venous twisting distal to
teries, and have an inconspicuous or absent light reflex. Fol- the artery, forming a dark, wide knuckle; Fig. 10-3G). 8,17
A Normal retinal artery and arteriovenous (A-V) crossing
Arterial wall (invisible) The normal arterial wall is Because the arterial wall
transparent. Only the column of Vein is transparent, a vein
Column of blood
blood within it can usually be crossing beneath the
seen. The normal light reflex is Arterial wall artery can be seen right
Light reflex
narrow–about 1/4 the diameter Artery up to the column of blood
of the blood column. on either side.
B Spasm and thickening of arterial walls C Silver wire arteries D Copper wire arteries
Narrowed column
of blood
Focal
narrowing Narrowed light
reflex
In hypertension, the arteries may show areas of Occasionally a portion of a Sometimes the arteries, especially
focal or generalized narrowing. The light reflex is narrowed artery develops such an those close to the disc, become full
also narrowed. Over many months or years, the opaque wall that no blood is visible and somewhat tortuous and develop
arterial wall thickens and becomes less within it. It is then called a silver an increased light reflex with a bright
y
y
transparent. wire artery. This change typically coppery luster. Such a vessel is called
y
y
occurs in the smallest branches. a copper wire artery.
E Tapering F Concealment or A-V nicking G Banking
The vein The vein The vein is
appears to taper appears to twisted on the
down on either stop abruptly distal side of
side of the on either side the artery and
artery. of the artery. forms a dark,
wide knuckle.
■ Figure 10-3 Vascular changes associated with high blood pressure. (A) Normal. (B) Spasm and thicken-
ing of arteriolar walls. (C) Silver wire arterioles. (D) Copper wire arterioles. (E) Venous tapering. (F) Arteri-
ovenous nicking. (G) Venous banking.