Page 293 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 293
Pa
Pa
M
M
g
e 2
e 2
g
g
8 P
/09
/09
/29
/29
1
1:1
8 P
1
1:1
69
a
a
ara
a
a
c.
c.
In
In
ara
A
p
69
A
p
t
ara
p
t
6
12_
0-c
12_
26
26
0-c
LWB
LWBK340-c12_ p p pp267-276.qxd 6/29/09 11:18 PM Page 269 Aptara Inc.
LWB
K34
K34
7-2
xd
xd
q
76.
q
q
76.
7-2
6
6
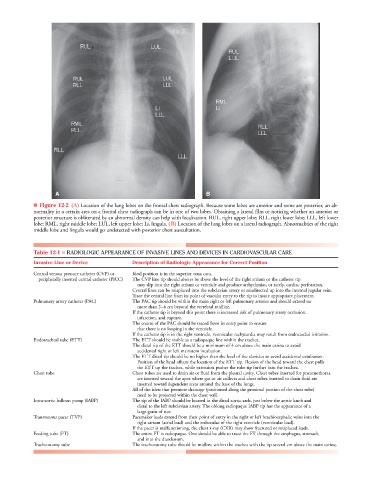
A B
■ Figure 12-2 (A) Location of the lung lobes on the frontal chest radiograph. Because some lobes are anterior and some are posterior, an ab-
normality in a certain area on a frontal chest radiograph can be in one of two lobes. Obtaining a lateral film or noticing whether an anterior or
posterior structure is obliterated by an abnormal density can help with localization. RUL, right upper lobe; RLL, right lower lobe; LLL, left lower
lobe; RML, right middle lobe; LUL, left upper lobe; Li, lingula. (B) Location of the lung lobes on a lateral radiograph. Abnormalities of the right
middle lobe and lingula would go undetected with posterior chest auscultation.
Table 12-1 ■ RADIOLOGIC APPEARANCE OF INVASIVE LINES AND DEVICES IN CARDIOVASCULAR CARE
Invasive Line or Device Description of Radiologic Appearance for Correct Position
Central venous pressure catheter (CVP) or Ideal position is in the superior vena cava.
peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) The CVP line tip should always be above the level of the right atrium or the catheter tip
may slip into the right atrium or ventricle and produce arrhythmias, or rarely, cardiac perforation.
Central lines can be misplaced into the subclavian artery or misdirected up into the internal jugular vein.
Trace the central line from its point of vascular entry to the tip to insure appropriate placement.
Pulmonary artery catheter (PAC) The PAC tip should be within the main right or left pulmonary arteries and should extend no
more than 2–4 cm beyond the vertebral midline.
If the catheter tip is beyond this point there is increased risk of pulmonary artery occlusion,
infarction, and rupture.
The course of the PAC should be traced from its entry point to ensure
that there is no looping in the ventricle.
If the catheter tip is in the right ventricle, ventricular tachycardia may result from endocardial irritation.
Endotracheal tube (ETT) The ETT should be visible as a radiopaque line within the trachea.
The distal tip of the ETT should be a minimum of 4 cm above the main carina to avoid
accidental right or left mainstem intubation.
The ETT distal tip should be no higher than the level of the clavicles to avoid accidental extubation.
Position of the head affects the location of the ETT tip. Flexion of the head toward the chest pulls
the ETT up the trachea, while extension pushes the tube tip further into the trachea.
Chest tube Chest tubes are used to drain air or fluid from the pleural cavity. Chest tubes inserted for pneumothorax
are inserted toward the apex where gas or air collects and chest tubes inserted to drain fluid are
inserted toward dependent areas around the base of the lungs.
All of the islets that promote drainage (positioned along the proximal portion of the chest tube)
need to be projected within the chest wall.
Intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) The tip of the IABP should be located in the distal aortic arch, just below the aortic knob and
distal to the left subclavian artery. The oblong radiopaque IABP tip has the appearance of a
large grain of rice.
Transvenous pacer (TVP) Pacemaker leads extend from their point of entry in the right or left brachiocephalic veins into the
right atrium (atrial lead) and the trabeculae of the right ventricle (ventricular lead).
If the pacer is malfunctioning, the chest x-ray (CXR) may show fractured or misplaced leads.
Feeding tube (FT) The entire FT is radiopaque. One should be able to trace the FT through the esophagus, stomach,
and into the duodenum.
Tracheostomy tube The tracheostomy tube should be midline within the trachea with the tip several cm above the main carina.