Page 35 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 35
92806_c01.qxd 11/21/11 10:30 AM Page 11
CHAPTER 1 / Cardiac Anatomy and Physiology 11
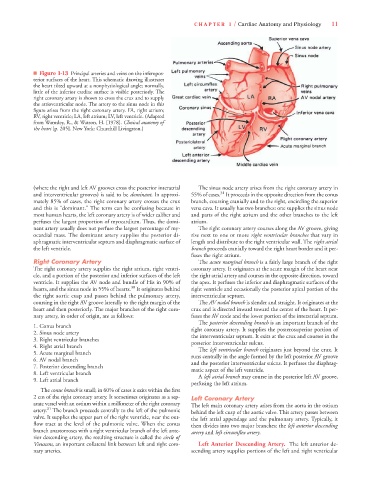
■ Figure 1-13 Principal arteries and veins on the inferopos-
terior surfaces of the heart. This schematic drawing illustrates
the heart tilted upward at a nonphysiological angle; normally,
little of the inferior cardiac surface is visible posteriorly. The
right coronary artery is shown to cross the crux and to supply
the atrioventricular node. The artery to the sinus node in this
figure arises from the right coronary artery. FA, right atrium;
RV, right ventricle; LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle. (Adapted
from Wamsley, R., & Watson, H. [1978]. Clinical anatomy of
the heart [p. 205]. New York: Churchill Livingston.)
(where the right and left AV grooves cross the posterior interatrial The sinus node artery arises from the right coronary artery in
31
and interventricular grooves) is said to be dominant. In approxi- 55% of cases. It proceeds in the opposite direction from the conus
mately 85% of cases, the right coronary artery crosses the crux branch, coursing cranially and to the right, encircling the superior
and this is “dominant.” The term can be confusing because in vena cava. It usually has two branches: one supplies the sinus node
most human hearts, the left coronary artery is of wider caliber and and parts of the right atrium and the other branches to the left
perfuses the largest proportion of myocardium. Thus, the domi- atrium.
nant artery usually does not perfuse the largest percentage of my- The right coronary artery courses along the AV groove, giving
ocardial mass. The dominant artery supplies the posterior di- rise next to one or more right ventricular branches that vary in
aphragmatic interventricular septum and diaphragmatic surface of length and distribute to the right ventricular wall. The right atrial
the left ventricle. branch proceeds cranially toward the right heart border and it per-
fuses the right atrium.
Right Coronary Artery The acute marginal branch is a fairly large branch of the right
The right coronary artery supplies the right atrium, right ventri- coronary artery. It originates at the acute margin of the heart near
cle, and a portion of the posterior and inferior surfaces of the left the right atrial artery and courses in the opposite direction, toward
ventricle. It supplies the AV node and bundle of His in 90% of the apex. It perfuses the inferior and diaphragmatic surfaces of the
30
hearts, and the sinus node in 55% of hearts. It originates behind right ventricle and occasionally the posterior apical portion of the
the right aortic cusp and passes behind the pulmonary artery, interventricular septum.
coursing in the right AV groove laterally to the right margin of the The AV nodal branch is slender and straight. It originates at the
heart and then posteriorly. The major branches of the right coro- crux and is directed inward toward the center of the heart. It per-
nary artery, in order of origin, are as follows: fuses the AV node and the lower portion of the interatrial septum.
The posterior descending branch is an important branch of the
1. Conus branch right coronary artery. It supplies the posterosuperior portion of
2. Sinus node artery the interventricular septum. It exits at the crux and courses in the
3. Right ventricular branches posterior interventricular sulcus.
4. Right atrial branch The left ventricular branch originates just beyond the crux. It
5. Acute marginal branch runs centrally in the angle formed by the left posterior AV groove
6. AV nodal branch and the posterior interventricular sulcus. It perfuses the diaphrag-
7. Posterior descending branch matic aspect of the left ventricle.
8. Left ventricular branch A left atrial branch may course in the posterior left AV groove,
9. Left atrial branch
perfusing the left atrium.
The conus branch is small; in 60% of cases it exits within the first
2 cm of the right coronary artery. It sometimes originates as a sep- Left Coronary Artery
arate vessel with an ostium within a millimeter of the right coronary The left main coronary artery arises from the aorta in the ostium
31
artery. The branch proceeds centrally to the left of the pulmonic behind the left cusp of the aortic valve. This artery passes between
valve. It supplies the upper part of the right ventricle, near the out- the left atrial appendage and the pulmonary artery. Typically, it
flow tract at the level of the pulmonic valve. When the conus then divides into two major branches: the left anterior descending
branch anastomoses with a right ventricular branch of the left ante- artery and left circumflex artery.
rior descending artery, the resulting structure is called the circle of
Vieussens, an important collateral link between left and right coro- Left Anterior Descending Artery. The left anterior de-
nary arteries. scending artery supplies portions of the left and right ventricular