Page 34 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 34
92806_c01.qxd 11/21/11 10:30 AM Page 10
10 PA R T I / Anatomy and Physiology
Table 1-1 ■ AREA SUPPLIED BY COMMON ARTERIES*
Structure Usual Arterial Supply Common Variants
Right atrium Sinus node artery, branch of RCA (55%) Sinus node artery, branch of L circumflex (45%)
Left atrium Major L circumflex † Sinus node artery, branch of L circumflex (45%)
Right ventricle
Anterior Major RCA
Minor LAD
Posterior Major RCA; posterior descending branch of RCA Posterior descending may branch from L circumflex (10%)
Minor LAD (ascending portion) LAD terminates at apex (40%)
Left Ventricle
Posterior (diaphragmatic) Major L circumflex, posterior descending branch of RCA Posterior descending may branch from L circumflex (10%)
Minor LAD (ascending portion) LAD terminates at apex (40%)
Anterior L coronary artery; L circumflex and LAD
Apex Major LAD
Intraventricular septum Major septal branches of LAD Minor posterior descending may branch from L circumflex,
AV nodal may branch from L circumflex
Minor posterior descending branch of RCA
and AV nodal branch of RCA
Left ventricular papillary muscles
Anterior Diagonal branch of LAD; other branches of LAD, Diagonal may branch from circumflex
other branches of L circumflex
Posterior RCA and L circumflex RCA and LAD
Sinus node Nodal artery from RCA (55%) Nodal artery from L circumflex (45%)
AV node RCA (90%) L circumflex (10%)
Bundle of His RCA (90%) L circumflex (10%)
Right bundle Major LAD septal branches
Minor AV nodal artery
Left anterior bundle Major LAD septal branches
Minor AV nodal artery
Left posterior bundle LAD septal branches and AV nodal artery
* Percentages in parentheses denote frequency of occurrence in autopsy studies.
† Major and minor refer to degree of predominance of an artery in perfusing a structure.
RCA, right coronary artery; LAD, left anterior descending artery; L, left; LV, left ventricle; AV, atrioventricular.
Data from James, T. N. (1961). Anatomy of the coronary arteries. New York: Paul B. Hoeber; James, T. N. (1978). Anatomy of the coronary arteries and veins. In J. W. Hurst (Ed.),
The heart (4th ed., pp. 32–47). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Individual anatomic variation should be considered in analyz- Also, apparently attenuated or narrowed vessels may be normal
ing patient data. For example, angiographic visualization of the left anatomic variants.
circumflex artery might show severe stenosis. Although it is not
likely that AV node and His bundle perfusion would be affected Vessel Dominance
(because the right coronary artery typically perfuses these struc- Dominance (or preponderance), a term commonly used in describ-
tures), in approximately 10% of cases the structures would be at ing coronary vasculature, refers to the distribution of the terminal
risk. Thus, angiographic information is validated with clinical data. portion of the arteries. The artery that reaches and crosses the crux
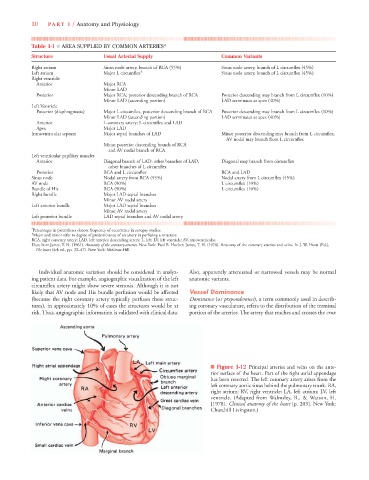
■ Figure 1-12 Principal arteries and veins on the ante-
rior surface of the heart. Part of the right atrial appendage
has been resected. The left coronary artery arises from the
left coronary aortic sinus behind the pulmonary trunk. RA,
right atrium; RV, right ventricle; LA, left atrium; LV, left
ventricle. (Adapted from Walmsley, R., & Watson, H.
[1978]. Clinical anatomy of the heart [p. 203]. New York:
Churchill Livingston.)