Page 32 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 32
92806_c01.qxd 11/21/11 10:30 AM Page 8
8 PA R T I / Anatomy and Physiology
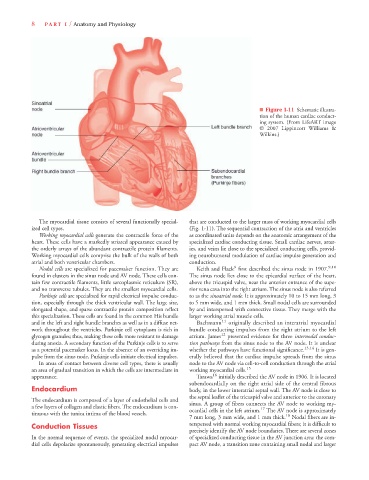
■ Figure 1-11 Schematic illustra-
tion of the human cardiac conduct-
ing system. (From LifeART image
© 2007 Lippincott Williams &
Wilkins.)
The myocardial tissue consists of several functionally special- that are conducted to the larger mass of working myocardial cells
ized cell types. (Fig. 1-11). The sequential contraction of the atria and ventricles
Working myocardial cells generate the contractile force of the as coordinated units depends on the anatomic arrangement of the
heart. These cells have a markedly striated appearance caused by specialized cardiac conducting tissue. Small cardiac nerves, arter-
the orderly arrays of the abundant contractile protein filaments. ies, and veins lie close to the specialized conducting cells, provid-
Working myocardial cells comprise the bulk of the walls of both ing neurohumoral modulation of cardiac impulse generation and
atrial and both ventricular chambers. conduction.
9
Nodal cells are specialized for pacemaker function. They are Keith and Flack first described the sinus node in 1907. 9,10
found in clusters in the sinus node and AV node. These cells con- The sinus node lies close to the epicardial surface of the heart,
tain few contractile filaments, little sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), above the tricuspid valve, near the anterior entrance of the supe-
and no transverse tubules. They are the smallest myocardial cells. rior vena cava into the right atrium. The sinus node is also referred
Purkinje cells are specialized for rapid electrical impulse conduc- to as the sinoatrial node. It is approximately 10 to 15 mm long, 3
tion, especially through the thick ventricular wall. The large size, to 5 mm wide, and 1 mm thick. Small nodal cells are surrounded
elongated shape, and sparse contractile protein composition reflect by and interspersed with connective tissue. They merge with the
this specialization. These cells are found in the common His bundle larger working atrial muscle cells.
and in the left and right bundle branches as well as in a diffuse net- Bachmann 11 originally described an interatrial myocardial
work throughout the ventricles. Purkinje cell cytoplasm is rich in bundle conducting impulses from the right atrium to the left
glycogen granules; thus, making these cells more resistant to damage atrium. James 12 presented evidence for three internodal conduc-
during anoxia. A secondary function of the Purkinje cells is to serve tion pathways from the sinus node to the AV node. It is unclear
as a potential pacemaker locus. In the absence of an overriding im- whether the pathways have functional significance. 13,14 It is gen-
pulse from the sinus node, Purkinje cells initiate electrical impulses. erally believed that the cardiac impulse spreads from the sinus
In areas of contact between diverse cell types, there is usually node to the AV node via cell-to-cell conduction through the atrial
an area of gradual transition in which the cells are intermediate in working myocardial cells. 15
appearance. Tarawa 16 initially described the AV node in 1906. It is located
subendocardially on the right atrial side of the central fibrous
Endocardium body, in the lower interatrial septal wall. The AV node is close to
the septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve and anterior to the coronary
The endocardium is composed of a layer of endothelial cells and
sinus. A group of fibers connects the AV node to working my-
a few layers of collagen and elastic fibers. The endocardium is con- 17
ocardial cells in the left atrium. The AV node is approximately
tinuous with the tunica intima of the blood vessels. 18
7 mm long, 3 mm wide, and 1 mm thick. Nodal fibers are in-
Conduction Tissues terspersed with normal working myocardial fibers; it is difficult to
precisely identify the AV node boundaries. There are several zones
In the normal sequence of events, the specialized nodal myocar- of specialized conducting tissue in the AV junction area: the com-
dial cells depolarize spontaneously, generating electrical impulses pact AV node, a transition zone containing small nodal and larger