Page 407 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 407
Pa
Pa
M
M
g
e 3
e 3
g
g
/09
1
c.
/09
1
6 A
6 A
2:1
2:1
ara
a
t
ara
a
c.
c.
In
In
A
A
83
83
A
p
t
p
p
q
q
87.
3-3
87.
6
6
xd
q
xd
3-3
K34
0-c
LWBK340-c16_
LWB K34 0-c 16_ pp333-387.qxd 6/30/09 12:16 AM Page 383 Aptara Inc.
LWB
33
33
p
16_
p
/30
/30
6
C HAPTER 1 6 / Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 383
V 1 1
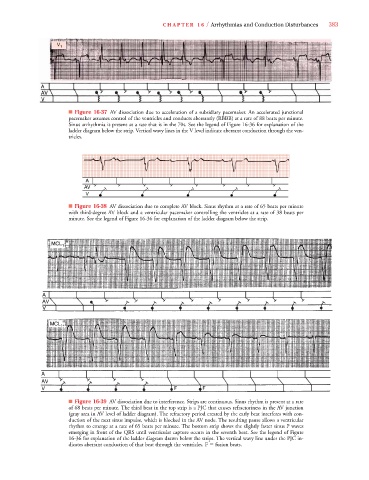
■ Figure 16-37 AV dissociation due to acceleration of a subsidiary pacemaker. An accelerated junctional
pacemaker assumes control of the ventricles and conducts aberrantly (RBBB) at a rate of 88 beats per minute.
Sinus arrhythmia is present at a rate that is in the 70s. See the legend of Figure 16-36 for explanation of the
ladder diagram below the strip. Vertical wavy lines in the V level indicate aberrant conduction through the ven-
tricles.
A
AV
V
■ Figure 16-38 AV dissociation due to complete AV block. Sinus rhythm at a rate of 65 beats per minute
with third-degree AV block and a ventricular pacemaker controlling the ventricles at a rate of 38 beats per
minute. See the legend of Figure 16-36 for explanation of the ladder diagram below the strip.
■ Figure 16-39 AV dissociation due to interference. Strips are continuous. Sinus rhythm is present at a rate
of 68 beats per minute. The third beat in the top strip is a PJC that causes refractoriness in the AV junction
(gray area in AV level of ladder diagram). The refractory period created by the early beat interferes with con-
duction of the next sinus impulse, which is blocked in the AV node. The resulting pause allows a ventricular
rhythm to emerge at a rate of 65 beats per minute. The bottom strip shows the slightly faster sinus P waves
emerging in front of the QRS until ventricular capture occurs in the seventh beat. See the legend of Figure
16-36 for explanation of the ladder diagram drawn below the strips. The vertical wavy line under the PJC in-
dicates aberrant conduction of that beat through the ventricles. F fusion beats.