Page 541 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 541
xd
Pa
q
xd
3
3
3
q
36.
g
1-5
36.
q
Pa
g
009
009
0 A
1:0
1:0
1
1
0 A
6/2
0/0
0/0
6/2
M
M
6/2
ara
ara
LWBK340-c22_
t
t
ara
K34
51
51
22_
0-c
0-c
22_
LWB
17
17
17
e 5
1-5
g
e 5
LWB K34 0-c 22_ p p pp511-536.qxd 30/06/2009 11:00 AM Page 517 Aptara
p
p
p
A
A
C HAPTER 22 / Acute Coronary Syndromes 517
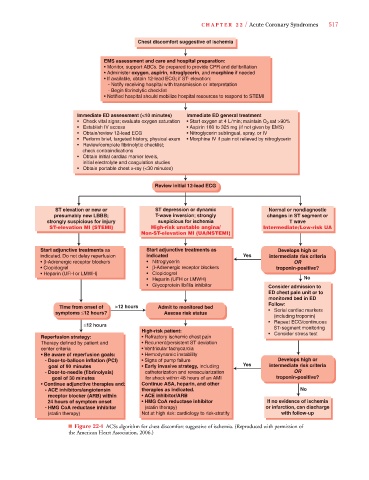
Chest discomfort suggestive of ischemia
EMS assessment and care and hospital preparation:
• Monitor, support ABCs. Be prepared to provide CPR and defibrillation
• Administer oxygen, aspirin, nitroglycerin, and morphine if needed
• If available, obtain 12-lead ECG; if ST- elevation:
- Notify receiving hospital with transmission or interpretation
- Begin fibrinolytic checklist
• Notified hospital should mobilize hospital resources to respond to STEMI
Immediate ED assessment (<10 minutes) Immediate ED general treatment
• Check vital signs; evaluate oxygen saturation • Start oxygen at 4 L/min; maintain O sat >90%
2
• Establish IV access • Aspirin 160 to 325 mg (if not given by EMS)
• Obtain/review 12-lead ECG • Nitroglycerin sublingual, spray, or IV
• Perform brief, targeted history, physical exam • Morphine IV if pain not relieved by nitroglycerin
• Review/complete fibrinolytic checklist;
check contraindications
• Obtain initial cardiac marker levels,
initial electrolyte and coagulation studies
• Obtain portable chest x-ray (<30 minutes)
Review initial 12-lead ECG
ST elevation or new or ST depression or dynamic Normal or nondiagnostic
presumably new LBBB; T-wave inversion; strongly changes in ST segment or
strongly suspicious for injury suspicious for ischemia T wave
ST-elevation MI (STEMI) High-risk unstable angina/ Intermediate/Low-risk UA
Non-ST-elevation MI (UA/NSTEMI)
Start adjunctive treatments as Start adjunctive treatments as Develops high or
indicated. Do not delay reperfusion indicated Yes intermediate risk criteria
• β-Adrenergic receptor blockers • Nitroglycerin OR
• Clopidogrel • β-Adrenergic receptor blockers troponin-positive?
• Heparin (UFH or LMWH) • Clopidogrel
• Heparin (UFH or LMWH) No
• Glycoprotein llb/llla inhibitor Consider admission to
ED chest pain unit or to
monitored bed in ED
Follow:
Time from onset of >12 hours Admit to monitored bed
symptoms ≤12 hours? Assess risk status • Serial cardiac markers
(including troponin)
• Repeat ECG/continuous
≤12 hours
ST-segment monitoring
High-risk patient:
Reperfusion strategy: • Refractory ischemic chest pain • Consider stress test
Therapy defined by patient and • Recurrent/persistent ST deviation
center criteria • Ventricular tachycardia
• Be aware of reperfusion goals: • Hemodynamic instability
- Door-to-balloon inflation (PCI) • Signs of pump failure Develops high or
goal of 90 minutes • Early invasive strategy, including Yes intermediate risk criteria
- Door-to-needle (fibrinolysis) catheterization and revascularization OR
goal of 30 minutes for shock within 48 hours of an AMI troponin-positive?
• Continue adjunctive therapies and : Continue ASA, heparin, and other
- ACE inhibitors/angiotensin therapies as indicated. No
receptor blocker (ARB) within • ACE inhibitor/ARB
24 hours of symptom onset • HMG CoA reductase inhibitor If no evidence of ischemia
- HMG CoA reductase inhibitor (statin therapy) or infarction, can discharge
(statin therapy) Not at high risk: cardiology to risk-stratify with follow-up
■ Figure 22-4 ACSs algorithm for chest discomfort suggestive of ischemia. (Reproduced with permission of
the American Heart Association, 2006.)