Page 715 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 715
qxd
qxd
04.
04.
/1/
/1/
7
7
tar
tar
Ap
Ap
5-7
5-7
p65
p65
09
g
g
a
a
691
691
e
e
49
49
09
9:
P
P
AM
AM
0-c
28_
28_
0-c
K34
LWBK340-c28_p655-704.qxd 7/1/09 9:9:49 AM Page 691 Aptara a a
K34
C HAPTER 2 8 / Pacemakers and Implantable Defibrillators 691
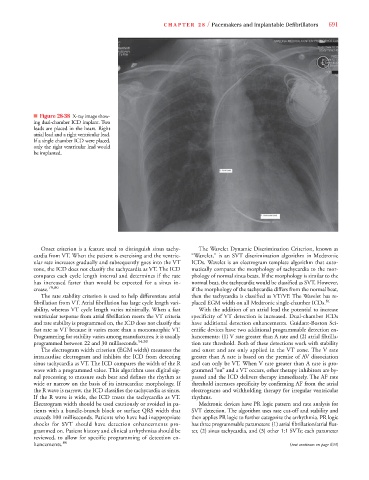
■ Figure 28-38 X-ray image show-
ing dual-chamber ICD implant. Two
leads are placed in the heart. Right
atrial lead and a right ventricular lead.
If a single chamber ICD were placed,
only the right ventricular lead would
be implanted.
Onset criterion is a feature used to distinguish sinus tachy- The Wavelet Dynamic Discrimination Criterion, known as
cardia from VT. When the patient is exercising and the ventric- “Wavelet,” is an SVT discrimination algorithm in Medtronic
ular rate increases gradually and subsequently goes into the VT ICDs. Wavelet is an electrogram template algorithm that auto-
zone, the ICD does not classify the tachycardia as VT. The ICD matically compares the morphology of tachycardia to the mor-
compares each cycle length interval and determines if the rate phology of normal sinus beats. If the morphology is similar to the
has increased faster than would be expected for a sinus in- normal beat, the tachycardia would be classified as SVT. However,
crease. 79,80 if the morphology of the tachycardia differs from the normal beat,
The rate stability criterion is used to help differentiate atrial then the tachycardia is classified as VT/VF. The Wavelet has re-
fibrillation from VT. Atrial fibrillation has large cycle length vari- placed EGM width on all Medtronic single-chamber ICDs. 81
ability, whereas VT cycle length varies minimally. When a fast With the addition of an atrial lead the potential to increase
ventricular response from atrial fibrillation meets the VT criteria specificity of VT detection is increased. Dual-chamber ICDs
and rate stability is programmed on, the ICD does not classify the have additional detection enhancements. Guidant-Boston Sci-
fast rate as VT because it varies more than a monomorphic VT. entific devices have two additional programmable detection en-
Programming for stability varies among manufactures; it is usually hancements: (1) V rate greater than A rate and (2) atrial fibrilla-
programmed between 22 and 30 milliseconds. 54,80 tion rate threshold. Both of these detections work with stability
The electrogram width criterion (EGM width) measures the and onset and are only applied in the VT zone. The V rate
intracardiac electrogram and inhibits the ICD from detecting greater than A rate is based on the premise of AV dissociation
sinus tachycardia as VT. The ICD compares the width of the R and can only be VT. When V rate greater than A rate is pro-
wave with a programmed value. This algorithm uses digital sig- grammed “on” and a VT occurs, other therapy inhibitors are by-
nal processing to measure each beat and defines the rhythm as passed and the ICD delivers therapy immediately. The AF rate
wide or narrow on the basis of its intracardiac morphology. If threshold increases specificity by confirming AF from the atrial
the R wave is narrow, the ICD classifies the tachycardia as sinus. electrograms and withholding therapy for irregular ventricular
If the R wave is wide, the ICD treats the tachycardia as VT. rhythms.
Electrogram width should be used cautiously or avoided in pa- Medtronic devices have PR logic pattern and rate analysis for
tients with a bundle-branch block or surface QRS width that SVT detection. The algorithm uses rate cut-off and stability and
exceeds 100 milliseconds. Patients who have had inappropriate then applies PR logic to further categorize the arrhythmia. PR logic
shocks for SVT should have detection enhancements pro- has three programmable parameters: (1) atrial fibrillation/atrial flut-
grammed on. Patient history and clinical arrhythmias should be ter, (2) sinus tachycardia, and (3) other 1:1 SVTs; each parameter
reviewed, to allow for specific programming of detection en-
hancements. 80 (text continues on page 693)