Page 831 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 831
LWBK340-c35_p799-822.qxd 29/06/2009 08:59 PM Page 807 Aptara
C HAPTER 35 / Hypertension 807
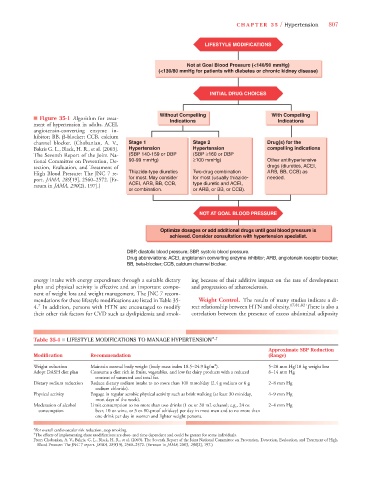
LIFESTYLE MODIFICATIONS
Not at Goal Blood Pressure (<140/90 mmHg)
(<130/80 mmHg for patients with diabetes or chronic kidney disease)
INITIAL DRUG CHOICES
Without Compelling With Compelling
■ Figure 35-1 Algorithm for treat- Indications Indications
ment of hypertension in adults. ACEI,
angiotensin-converting enzyme in-
hibitor; BB, -blocker; CCB, calcium
channel blocker. (Chobanian, A. V., Stage 1 Stage 2 Drug(s) for the
Bakris G. L., Black, H. R., et al. [2003]. Hypertension Hypertension compelling indications
The Seventh Report of the Joint Na- (SBP 140-159 or DBP (SBP ≥160 or DBP
tional Committee on Prevention, De- 90-99 mmHg) ≥100 mmHg) Other antihypertensive
tection, Evaluation, and Treatment of drugs (diuretics, ACEI,
High Blood Pressure: The JNC 7 re- Thiazide-type diuretics Two-drug combination ARB, BB, CCB) as
port. JAMA, 289[19], 2560–2572. [Er- for most. May consider for most (usually thiazide- needed.
ratum in JAMA, 290(2), 197].) ACEI, ARB, BB, CCB, type diuretic and ACEI,
or combination. or ARB, or BB, or CCB).
NOT AT GOAL BLOOD PRESSURE
Optimize dosages or add additional drugs until goal blood pressure is
achieved. Consider consultation with hypertension specialist.
DBP, diastolic blood pressure; SBP, systolic blood pressure.
Drug abbreviations: ACEI, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker;
BB, beta-blocker; CCB, calcium channel blocker.
energy intake with energy expenditure through a suitable dietary ing because of their additive impact on the rate of development
plan and physical activity is effective and an important compo- and progression of atherosclerosis.
nent of weight loss and weight management. The JNC 7 recom-
mendations for these lifestyle modifications are listed in Table 35- Weight Control. The results of many studies indicate a di-
7
4. In addition, persons with HTN are encouraged to modify rect relationship between HTN and obesity. 17,81,82 There is also a
their other risk factors for CVD such as dyslipidemia and smok- correlation between the presence of excess abdominal adiposity
Table 35-4 ■ LIFESTYLE MODIFICATIONS TO MANAGE HYPERTENSION* ,†
Approximate SBP Reduction
Modification Recommendation (Range)
2
Weight reduction Maintain normal body weight (body mass index 18.5–24.9 kg/m ). 5–20 mm Hg/10 kg weight loss
Adopt DASH diet plan Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and low fat dairy products with a reduced 8–14 mm Hg
content of saturated and total fat.
Dietary sodium reduction Reduce dietary sodium intake to no more than 100 mmol/day (2.4 g sodium or 6 g 2–8 mm Hg
sodium chloride).
Physical activity Engage in regular aerobic physical activity such as brisk walking (at least 30 min/day, 4–9 mm Hg
most days of the week).
Moderation of alcohol Limit consumption to no more than two drinks (1 oz or 30 mL ethanol; e.g., 24 oz 2–4 mm Hg
consumption beer, 10 oz wine, or 3 oz 80-proof whiskey) per day in most men and to no more than
one drink per day in women and lighter weight persons.
*For overall cardiovascular risk reduction, stop smoking.
†
The effects of implementing these modifications are dose- and time dependent and could be greater for some individuals.
From Chobanian, A. V., Bakris, G. L., Black, H. R., et al. (2003). The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High
Blood Pressure: The JNC 7 report. JAMA, 289(19), 2560–2572. (Erratum in JAMA, 2003, 290[2], 197.)