Page 835 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 835
/
0
6
9
8:
8:
9
2
22.
9-8
9 P
p79
qx
qx
d
e 8
11
Apt
g
M
Pa
Pa
Apt
2
5
0
009
ar
a
009
3
0-c
5
3
LWB
L L LWB K34 0-c 3 5 _ _ p79 9-8 22. qx d 2 9 / 0 6 / / 2 009 0 8: 5 9 P M Pa g e 8 11 Apt ar a
K34
LWBK340-c35_p799-822.qxd 29/06/2009 08:59 PM Page 811 Aptara
C HAPTER 35 / Hypertension 811
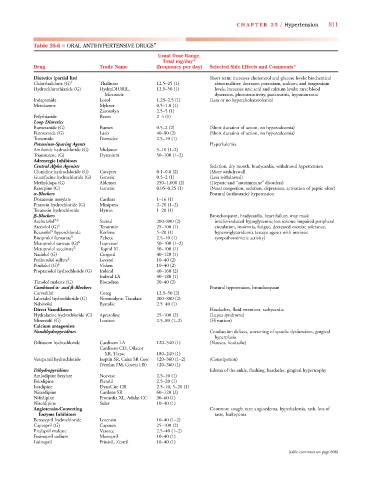
Table 35-6 ■ ORAL ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS*
Usual Dose Range,
Total mg/day*
Drug Trade Name (frequency per day) Selected Side Effects and Comments*
Diuretics (partial list) Short term: increases cholesterol and glucose levels; biochemical
Chlorthalidone (G) † Thalitone 12.5–25 (1) abnormalities: decreases potassium, sodium, and magnesium
Hydrochlorothiazide (G) HydroDIURIL, 12.5–50 (1) levels, increases uric acid and calcium levels; rare: blood
Microzide dyscrasias, photosensitivity, pancreatitis, hyponatremia
Indapamide Lozol 1.25–2.5 (1) (Less or no hypercholesterolemia)
Metolazone Mykrox 0.5–1.0 (1)
Zaroxolyn 2.5–5 (1)
Polythiazide Renes 2–4 (1)
Loop Diuretics
Bumetanide (G) Bumex 0.5–2 (2) (Short duration of action, no hypercalcemia)
Furosemide (G) Lasix 40–80 (2) (Short duration of action, no hypercalcemia)
Torsemide Demadex 2.5–10 (1)
Potassium-Sparing Agents Hyperkalemia
Amiloride hydrochloride (G) Midamor 5–10 (1–2)
Triamterene (G) Dyrenium 50–100 (1–2)
Adrenergic Inhibitors
Central Alpha Agonists Sedation, dry mouth, bradycardia, withdrawal hypertension
Clonidine hydrochloride (G) Catapres 0.1–0.8 (2) (More withdrawal)
Guanfacine hydrochloride (G) Generic 0.5–2 (1) (Less withdrawal)
Methyldopa (G) Aldomet 250–1,000 (2) (Hepatic and “autoimmune” disorders)
Reserpine (G) Generic 0.05–0.25 (1) (Nasal congestion, sedation, depression, activation of peptic ulcer)
-Blockers Postural (orthostatic) hypotension
Doxazosin mesylate Cardura 1–16 (1)
Prazosin hydrochloride (G) Minipress 2–20 (1–2)
Terazosin hydrochloride Hytrin 1–20 (1)
-Blockers Bronchospasm, bradycardia, heart failure, may mask
Acebutolol ‡,§ Sectral 200–800 (2) insulin-induced hypoglycemia; less serious: impaired peripheral
Atenolol (G) § Tenormin 25–100 (1) circulation, insomnia, fatigue, decreased exercise tolerance,
§
Betaxolol hyperchloride Kerlone 5–20 (1) hypertriglyceridemia (except agents with intrinsic
Bisoprolol fumarate § Zebeta 2.5–10 (1) sympathomimetic activity)
Metoprolol tartrate (G) § Lopressor 50–100 (1–2)
Metoprolol succinate § Toprol XL 50–100 (1)
Nadolol (G) Corgard 40–120 (1)
Penbutolol sulfate ‡ Levatol 10–40 (2)
Pindolol (G) ‡ Visken 10–40 (2)
Propranolol hydrochloride (G) Inderal 40–160 (2)
Inderal LA 40–180 (1)
Timolol maleate (G) Blocadren 20–40 (2)
Combined - and -Blockers Postural hypotension, bronchospasm
Carvedilol Coreg 12.5–50 (2)
Labetalol hydrochloride (G) Normodyne, Trandate 200–800 (2)
Nebivolol Bystolic 2.5–40 (1)
Direct Vasodilators Headaches, fluid retention, tachycardia
Hydralazine hydrochloride (G) Apresoline 25–100 (2) (Lupus syndrome)
Minoxidil (G) Loniten 2.5–80 (1–2) (Hirsutism)
Calcium antagonists
Nondihydropyridines Conduction defects, worsening of systolic dysfunction, gingival
hyperplasia
Diltiazem hydrochloride Cardizem LA 120–540 (1) (Nausea, headache)
Cardizem CD, Dilacor
XR, Tiazac 180–240 (1)
Verapamil hydrochloride Isoptin SR, Calan SR Coer 120–360 (1–2) (Constipation)
(Verelan PM, Covera HS) 120–360 (1)
Dihydropyridines Edema of the ankle, flushing, headache, gingival hypertrophy
Amlodipine besylate Norvasc 2.5–10 (1)
Felodipine Plendil 2.5–20 (1)
Isradipine DynaCirc CR 2.5–10, 5–20 (1)
Nicardipine Cardene SR 60–120 (2)
Nifedipine Procardia XL, Adalat CC 30–60 (1)
Nisoldipine Sular 10–40 (1)
Angiotensin-Converting Common: cough; rare: angioedema, hyperkalemia, rash, loss of
Enzyme Inhibitors taste, leukopenia
Benazepril hydrochloride Lotensin 10–40 (1–2)
Captopril (G) Capoten 25–100 (2)
Enalapril maleate Vasotec 2.5–40 (1–2)
Fosinopril sodium Monopril 10–40 (1)
Lisinopril Prinivil, Zestril 10–40 (1)
(table continues on page 808)