Page 222 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 222
Cardiovascular Assessment and Monitoring 199
INVASIVE CARDIOVASCULAR MONITORING
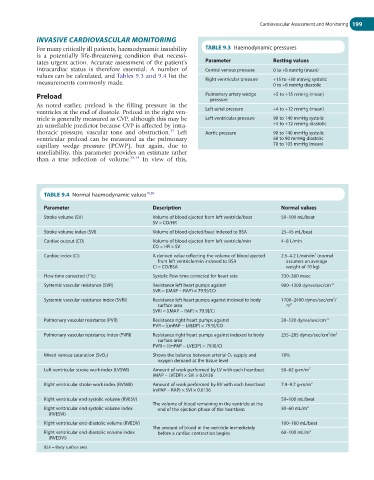
For many critically ill patients, haemodynamic instability TABLE 9.3 Haemodynamic pressures
is a potentially life-threatening condition that necessi-
tates urgent action. Accurate assessment of the patient’s Parameter Resting values
intracardiac status is therefore essential. A number of Central venous pressure 0 to +8 mmHg (mean)
values can be calculated, and Tables 9.3 and 9.4 list the
measurements commonly made. Right ventricular pressure +15 to +30 mmHg systolic
0 to +8 mmHg diastolic
Preload Pulmonary artery wedge +5 to +15 mmHg (mean)
pressure
As noted earlier, preload is the filling pressure in the
ventricles at the end of diastole. Preload in the right ven- Left atrial pressure +4 to +12 mmHg (mean)
tricle is generally measured as CVP, although this may be Left ventricular pressure 90 to 140 mmHg systolic
an unreliable predictor because CVP is affected by intra- +4 to +12 mmHg diastolic
thoracic pressure, vascular tone and obstruction. Left Aortic pressure 90 to 140 mmHg systolic
37
ventricular preload can be measured as the pulmonary 60 to 90 mmHg diastolic
capillary wedge pressure (PCWP), but again, due to 70 to 105 mmHg (mean)
unreliability, this parameter provides an estimate rather
than a true reflection of volume. 38,39 In view of this,
TABLE 9.4 Normal haemodynamic values 10,36
Parameter Description Normal values
Stroke volume (SV) Volume of blood ejected from left ventricle/beat 50–100 mL/beat
SV = CO/HR
Stroke volume index (SVI) Volume of blood ejected/beat indexed to BSA 25–45 mL/beat
Cardiac output (CO) Volume of blood ejected from left ventricle/min 4–8 L/min
CO = HR × SV
Cardiac index (CI) A derived value reflecting the volume of blood ejected 2.5–4.2 L/min/m (normal
2
from left ventricle/min indexed to BSA assumes an average
CI = CO/BSA weight of 70 kg)
Flow time corrected (FTc) Systolic flow time corrected for heart rate 330–360 msec
Systemic vascular resistance (SVR) Resistance left heart pumps against 900–1300 dynes/sec/cm −5
SVR = [(MAP − RAP) × 79.9]/CO
Systemic vascular resistance index (SVRI) Resistance left heart pumps against indexed to body 1700–2400 dynes/sec/cm /
5
surface area m 2
SVRI = [(MAP − RAP) × 79.9]/CI
Pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) Resistance right heart pumps against 20–120 dynes/sec/cm −5
PVR = [(mPAP − LVEDP) × 79.9]/CO
5
Pulmonary vascular resistance index (PVRI) Resistance right heart pumps against indexed to body 255–285 dynes/sec/cm /m 2
surface area
PVRI = [(mPAP − LVEDP) × 79.9]/CI
Mixed venous saturation (SvO 2 ) Shows the balance between arterial O 2 supply and 70%
oxygen demand at the tissue level
Left ventricular stroke work index (LVSWI) Amount of work performed by LV with each heartbeat 50–62 g-m/m 2
(MAP – LVEDP) × SVI × 0.0136
Right ventricular stroke work index (RVSWI) Amount of work performed by RV with each heartbeat 7.9–9.7 g-m/m 2
(mPAP – RAP) × SVI × 0.0136
Right ventricular end-systolic volume (RVESV) 50–100 mL/beat
The volume of blood remaining in the ventricle at the
Right ventricular end-systolic volume index end of the ejection phase of the heartbeat 30–60 mL/m 2
(RVESVI)
Right ventricular end-diastolic volume (RVEDV) 100–160 mL/beat
The amount of blood in the ventricle immediately
Right ventricular end-diastolic volume index before a cardiac contraction begins 60–100 mL/m 2
(RVEDVI)
BSA = Body surface area