Page 224 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 224
Cardiovascular Assessment and Monitoring 201
A
B
C
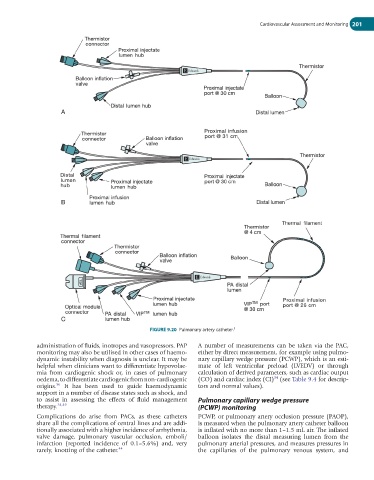
FIGURE 9.20 Pulmonary artery catheter. 5
administration of fluids, inotropes and vasopressors. PAP A number of measurements can be taken via the PAC,
monitoring may also be utilised in other cases of haemo- either by direct measurement, for example using pulmo-
dynamic instability when diagnosis is unclear. It may be nary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP), which is an esti-
helpful when clinicians want to differentiate hypovolae- mate of left ventricular preload (LVEDV) or through
mia from cardiogenic shock or, in cases of pulmonary calculation of derived parameters, such as cardiac output
34
oedema, to differentiate cardiogenic from non-cardiogenic (CO) and cardiac index (CI) (see Table 9.4 for descrip-
origins. It has been used to guide haemodynamic tors and normal values).
56
support in a number of disease states such as shock, and
to assist in assessing the effects of fluid management Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
therapy. 34,49 (PCWP) monitoring
Complications do arise from PACs, as these catheters PCWP, or pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP),
share all the complications of central lines and are addi- is measured when the pulmonary artery catheter balloon
tionally associated with a higher incidence of arrhythmia, is inflated with no more than 1–1.5 mL air. The inflated
valve damage, pulmonary vascular occlusion, emboli/ balloon isolates the distal measuring lumen from the
infarction (reported incidence of 0.1–5.6%) and, very pulmonary arterial pressures, and measures pressures in
rarely, knotting of the catheter. 44 the capillaries of the pulmonary venous system, and