Page 232 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 232
Cardiovascular Assessment and Monitoring 209
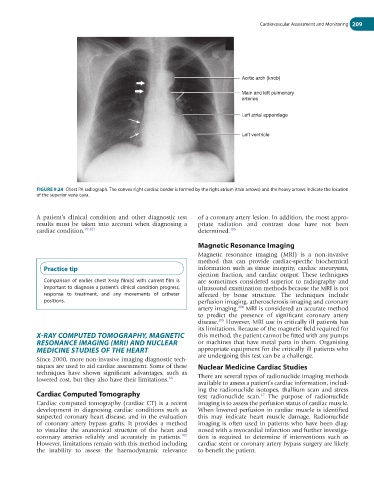
Aortic arch (knob)
Main and left pulmonary
arteries
Left atrial appendage
Left ventricle
FIGURE 9.24 Chest PA radiograph. The convex right cardiac border is formed by the right atrium (thin arrows) and the heavy arrows indicate the location
of the superior vena cava.
A patient’s clinical condition and other diagnostic test of a coronary artery lesion. In addition, the most appro-
results must be taken into account when diagnosing a priate radiation and contrast dose have not been
cardiac condition. 99,101 determined. 103
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive
method that can provide cardiac-specific biochemical
Practice tip information such as tissue integrity, cardiac aneurysms,
ejection fraction, and cardiac output. These techniques
Comparison of earlier chest X-ray film(s) with current film is are sometimes considered superior to radiography and
important to diagnose a patient’s clinical condition progress, ultrasound examination methods because the MRI is not
response to treatment, and any movements of catheter affected by bone structure. The techniques include
positions. perfusion imaging, atherosclerosis imaging and coronary
104
artery imaging. MRI is considered an accurate method
to predict the presence of significant coronary artery
disease. However, MRI use in critically ill patients has
105
its limitations. Because of the magnetic field required for
X-RAY COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY, MAGNETIC this method, the patient cannot be fitted with any pumps
RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI) AND NUCLEAR or machines that have metal parts in them. Organising
MEDICINE STUDIES OF THE HEART appropriate equipment for the critically ill patients who
Since 2000, more non-invasive imaging diagnostic tech- are undergoing this test can be a challenge.
niques are used to aid cardiac assessment. Some of these Nuclear Medicine Cardiac Studies
techniques have shown significant advantages, such as
lowered cost, but they also have their limitations. 66 There are several types of radionuclide imaging methods
available to assess a patient’s cardiac information, includ-
ing the radionuclide isotopes, thallium scan and stress
Cardiac Computed Tomography test radionuclide scan. The purpose of radionuclide
17
Cardiac computed tomography (cardiac CT) is a recent imaging is to assess the perfusion status of cardiac muscle.
development in diagnosing cardiac conditions such as When lowered perfusion in cardiac muscle is identified
suspected coronary heart disease, and in the evaluation this may indicate heart muscle damage. Radionuclide
of coronary artery bypass grafts. It provides a method imaging is often used in patients who have been diag-
to visualise the anatomical structure of the heart and nosed with a myocardial infarction and further investiga-
102
coronary arteries reliably and accurately in patients. tion is required to determine if interventions such as
However, limitations remain with this method including cardiac stent or coronary artery bypass surgery are likely
the inability to assess the haemodynamic relevance to benefit the patient.