Page 283 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 283
260 P R I N C I P L E S A N D P R A C T I C E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
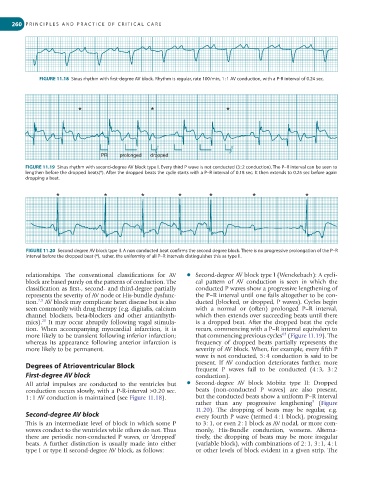
FIGURE 11.18 Sinus rhythm with first-degree AV block. Rhythm is regular, rate 100/min, 1 : 1 AV conduction, with a P-R interval of 0.24 sec.
* * *
PR prolonged dropped
FIGURE 11.19 Sinus rhythm with second-degree AV block type I. Every third P wave is not conducted (3 : 2 conduction). The P–R interval can be seen to
lengthen before the dropped beats(*). After the dropped beats the cycle starts with a P–R interval of 0.18 sec. It then extends to 0.25 sec before again
dropping a beat.
* * * * * * *
FIGURE 11.20 Second degree AV block type II. A non conducted beat confirms the second degree block. There is no progressive prolongation of the P–R
interval before the dropped beat (*), rather, the uniformity of all P–R intervals distinguishes this as type II.
relationships. The conventional classifications for AV ● Second-degree AV block type I (Wenckebach): A cycli-
block are based purely on the patterns of conduction. The cal pattern of AV conduction is seen in which the
classification as first-, second- and third-degree partially conducted P waves show a progressive lengthening of
represents the severity of AV node or His-bundle dysfunc- the P–R interval until one fails altogether to be con-
7,9
tion. AV block may complicate heart disease but is also ducted (blocked, or dropped, P waves). Cycles begin
seen commonly with drug therapy (e.g. digitalis, calcium with a normal or (often) prolonged P–R interval,
channel blockers, beta-blockers and other antiarrhyth- which then extends over succeeding beats until there
20
mics). It may occur abruptly following vagal stimula- is a dropped beat. After the dropped beat the cycle
tion. When accompanying myocardial infarction, it is recurs, commencing with a P–R interval equivalent to
63
more likely to be transient following inferior infarction; that commencing previous cycles (Figure 11.19). The
whereas its appearance following anterior infarction is frequency of dropped beats partially represents the
more likely to be permanent. severity of AV block. When, for example, every fifth P
wave is not conducted, 5 : 4 conduction is said to be
Degrees of Atrioventricular Block present. If AV conduction deteriorates further, more
frequent P waves fail to be conducted (4 : 3, 3 : 2
First-degree AV block conduction).
All atrial impulses are conducted to the ventricles but ● Second-degree AV block Mobitz type II: Dropped
conduction occurs slowly, with a P-R-interval >0.20 sec. beats (non-conducted P waves) are also present,
1 : 1 AV conduction is maintained (see Figure 11.18). but the conducted beats show a uniform P–R interval
9
rather than any progressive lengthening (Figure
11.20). The dropping of beats may be regular, e.g.
Second-degree AV block every fourth P wave (termed 4 : 1 block), progressing
This is an intermediate level of block in which some P to 3 : 1, or even 2 : 1 block as AV nodal, or more com-
waves conduct to the ventricles while others do not. Thus monly, His-Bundle conduction, worsens. Alterna-
there are periodic non-conducted P waves, or ‘dropped’ tively, the dropping of beats may be more irregular
beats. A further distinction is usually made into either (variable block), with combinations of 2 : 1, 3 : 1, 4 : 1
type I or type II second-degree AV block, as follows: or other levels of block evident in a given strip. The