Page 441 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 441
418 P R I N C I P L E S A N D P R A C T I C E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
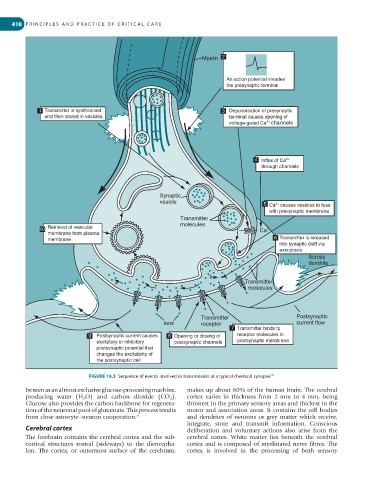
Myelin 2
An action potential invades
the presynaptic terminal
1 Transmitter is synthesised 3 Depolarisation of presynaptic
and then stored in vesicles terminal causes opening of
2+
voltage-gated Ca channels
4 Influx of Ca 2+
through channels
Synaptic
vesicle
2+
5 Ca causes vesicles to fuse
with presynaptic membrane
Transmitter
molecules
10 Retrieval of vesicular Ca 2+
membrane from plasma
membrane 6 Transmitter is released
into synaptic cleft via
exocytosis
Across
dendrite
Transmitter
molecules
Transmitter Postsynaptic
Ions receptor current flow
7 Transmitter binds tp
9 Postsynaptic current causes 8 Opening or closing of receptor molecules in
excitatory or inhibitory postsynaptic channels postsynaptic membrane
postsynaptic potential that
changes the excitability of
the postsynaptic cell
FIGURE 16.3 Sequence of events involved in transmission at a typical chemical synapse.
82
be seen as an almost exclusive glucose-processing machine, makes up about 80% of the human brain. The cerebral
producing water (H 2 O) and carbon dioxide (CO 2 ). cortex varies in thickness from 2 mm to 4 mm, being
Glucose also provides the carbon backbone for regenera- thinnest in the primary sensory areas and thickest in the
tion of the neuronal pool of glutamate. This process results motor and association areas. It contains the cell bodies
from close astrocyte–neuron cooperation. 11 and dendrites of neurons or grey matter which receive,
integrate, store and transmit information. Conscious
Cerebral cortex deliberation and voluntary actions also arise from the
The forebrain contains the cerebral cortex and the sub- cerebral cortex. White matter lies beneath the cerebral
cortical structures rostral (sideways) to the diencepha- cortex and is composed of myelinated nerve fibres. The
lon. The cortex, or outermost surface of the cerebrum, cortex is involved in the processing of both sensory