Page 443 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 443
420 P R I N C I P L E S A N D P R A C T I C E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
White
Cerebrum Grey matter
matter
Diencephalon Sympathetic chain
Ventral
root Sympathetic
Midbrain
chain ganglion
Pons
Dorsal root
Cerebellum ganglion
C1 Dorsal
2 Medulla root
3 Layers of
Cervical 4 dura mater
nerves 5 Spinal cord
6
7
8 Cervical
T1 enlargement
2
3 Vertebra
4
5 Spinal
nerve
6
Thoracic 7
nerves
8
9
10
11
Lumbar
12 enlargement
L1
Cauda
Lumbar 2 equina
nerves
3
4
5
S1
Sacral 2
nerves 3
4
5
Coccygeal Coc 1
nerves
82
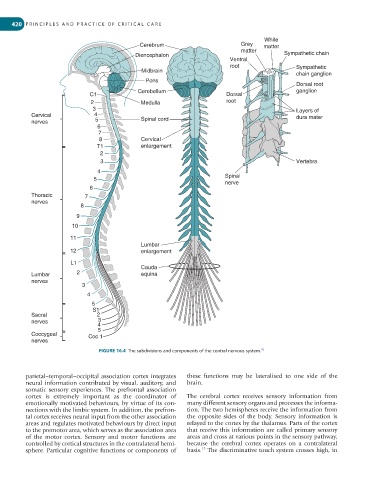
FIGURE 16.4 The subdivisions and components of the central nervous system.
parietal–temporal–occipital association cortex integrates these functions may be lateralised to one side of the
neural information contributed by visual, auditory, and brain.
somatic sensory experiences. The prefrontal association
cortex is extremely important as the coordinator of The cerebral cortex receives sensory information from
emotionally motivated behaviours, by virtue of its con- many different sensory organs and processes the informa-
nections with the limbic system. In addition, the prefron- tion. The two hemispheres receive the information from
tal cortex receives neural input from the other association the opposite sides of the body. Sensory information is
areas and regulates motivated behaviours by direct input relayed to the cortex by the thalamus. Parts of the cortex
to the premotor area, which serves as the association area that receive this information are called primary sensory
of the motor cortex. Sensory and motor functions are areas and cross at various points in the sensory pathway,
controlled by cortical structures in the contralateral hemi- because the cerebral cortex operates on a contralateral
13
sphere. Particular cognitive functions or components of basis. The discriminative touch system crosses high, in