Page 451 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 451
428 P R I N C I P L E S A N D P R A C T I C E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
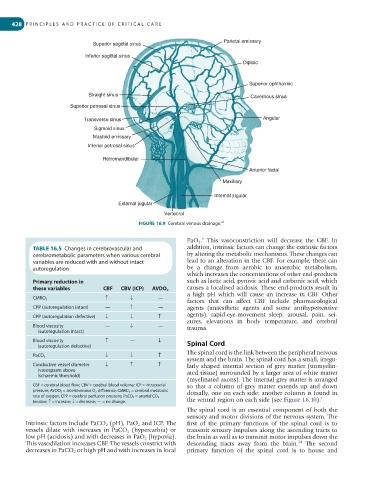
Parietal emissary
Superior sagittal sinus
Inferior sagittal sinus
Diploic
Superior ophthalmic
Straight sinus Cavernous sinus
Superior petrosal sinus
Transverse sinus Angular
Sigmoid sinus
Mastoid emissary
Inferior petrosal sinus
Retromandibular
Anterior facial
Maxillary
Internal jugular
External jugular
Vertebral
FIGURE 16.9 Cerebral venous drainage.
23
1
PaO 2 . This vasoconstriction will decrease the CBF. In
TABLE 16.5 Changes in cerebrovascular and addition, intrinsic factors can change the extrinsic factors
cerebrometabolic parameters when various cerebral by altering the metabolic mechanisms. These changes can
variables are reduced with and without intact lead to an alteration in the CBF. For example, there can
autoregulation be a change from aerobic to anaerobic metabolism,
which increases the concentrations of other end-products
Primary reduction in such as lactic acid, pyruvic acid and carbonic acid, which
these variables CBF CBV (ICP) AVDO 2 causes a localised acidosis. These end-products result in
a high pH which will cause an increase in CBF. Other
↑ ↓ —
factors that can affect CBF include pharmacological
CMRO 2
CPP (autoregulation intact) — ↑ — agents (anaesthetic agents and some antihypertensive
CPP (autoregulation defective) ↓ ↓ ↑ agents), rapid-eye-movement sleep, arousal, pain, sei-
zures, elevations in body temperature, and cerebral
Blood viscosity — ↓ — trauma.
(autoregulation intact)
Blood viscosity ↑ — ↓ Spinal Cord
(autoregulation defective)
The spinal cord is the link between the peripheral nervous
↓ ↓ ↑
PaCO 2
system and the brain. The spinal cord has a small, irregu-
Conductive vessel diameter ↓ ↑ ↑ larly shaped internal section of grey matter (unmyelin-
(vasospasm above ated tissue) surrounded by a larger area of white matter
ischaemic threshold)
(myelinated axons). The internal grey matter is arranged
CBF = cerebral blood flow; CBV = cerebral blood volume; ICP = intracranial so that a column of grey matter extends up and down
pressure; AVDO 2 = arteriovenous O 2 difference; CMRO 2 = cerebral metabolic dorsally, one on each side; another column is found in
rate of oxygen; CPP = cerebral perfusion pressure; PaCO 2 = arterial CO 2 1
tension; ↑ = increase; ↓ = decrease; — = no change. the ventral region on each side (see Figure 16.10).
The spinal cord is an essential component of both the
sensory and motor divisions of the nervous system. The
Intrinsic factors include PaCO 2 (pH), PaO 2 and ICP. The first of the primary functions of the spinal cord is to
vessels dilate with increases in PaCO 2 (hypercarbia) or transmit sensory impulses along the ascending tracts to
low pH (acidosis) and with decreases in PaO 2 (hypoxia). the brain as well as to transmit motor impulses down the
24
This vasodilation increases CBF. The vessels constrict with descending tracts away from the brain. The second
decreases in PaCO 2 or high pH and with increases in local primary function of the spinal cord is to house and