Page 450 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 450
Neurological Assessment and Monitoring 427
Anterior
Anterior cerebral artery
cerebral
artery
Middle
cerebral
artery
Internal
carotid Portion of
artery temporal
lobe
removed
Basilar
artery Posterior
inferior Middle
Anterior cerebellar cerebral
inferior artery Posterior artery
cerebellar cerebral artery
artery Vertebral B
artery
Anterior
communicating Posterior
artery
communicating
artery
Posterior
cerebral artery Anterior
(to midbrain) cerebral
C Posterior artery
Basilar artery cerebral
(to pons) artery
A
Lenticulostriate
arteries
Anterior
cerebral
artery
Middle
cerebral
artery Anterior
Internal communicating
carotid artery
D artery
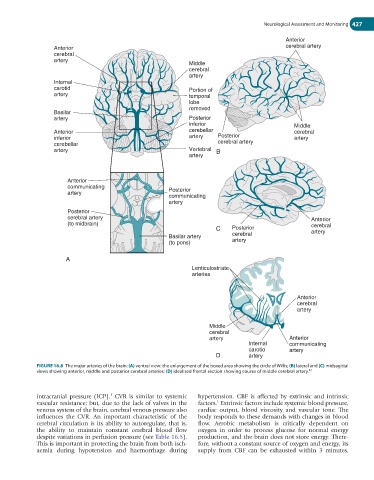
FIGURE 16.8 The major arteries of the brain: (A) ventral view: the enlargement of the boxed area showing the circle of Willis; (B) lateral and (C) midsagittal
82
views showing anterior, middle and posterior cerebral arteries; (D) idealised frontal section showing course of middle cerebral artery.
1
intracranial pressure (ICP). CVR is similar to systemic hypertension. CBF is affected by extrinsic and intrinsic
1
vascular resistance; but, due to the lack of valves in the factors. Extrinsic factors include systemic blood pressure,
venous system of the brain, cerebral venous pressure also cardiac output, blood viscosity and vascular tone. The
influences the CVR. An important characteristic of the body responds to these demands with changes in blood
cerebral circulation is its ability to autoregulate, that is, flow. Aerobic metabolism is critically dependent on
the ability to maintain constant cerebral blood flow oxygen in order to process glucose for normal energy
despite variations in perfusion pressure (see Table 16.5). production, and the brain does not store energy. There-
This is important in protecting the brain from both isch- fore, without a constant source of oxygen and energy, its
aemia during hypotension and haemorrhage during supply from CBF can be exhausted within 3 minutes.