Page 452 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 452
Neurological Assessment and Monitoring 429
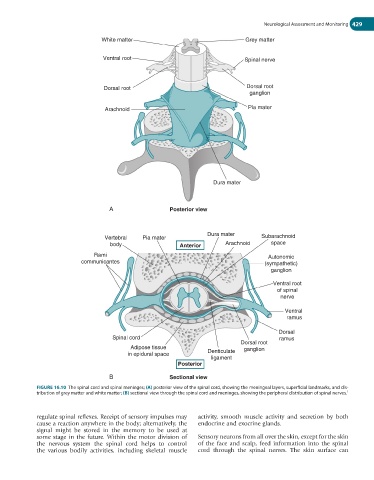
White matter Grey matter
Ventral root Spinal nerve
Dorsal root Dorsal root
ganglion
Arachnoid Pia mater
Dura mater
A Posterior view
Dura mater
Vertebral Pia mater Subarachnoid
body Anterior Arachnoid space
Rami Autonomic
communicantes (sympathetic)
ganglion
Ventral root
of spinal
nerve
Ventral
ramus
Dorsal
Spinal cord ramus
Dorsal root
Adipose tissue ganglion
in epidural space Denticulate
ligament
Posterior
B Sectional view
FIGURE 16.10 The spinal cord and spinal meninges; (A) posterior view of the spinal cord, showing the meningeal layers, superficial landmarks, and dis-
tribution of grey matter and white matter; (B) sectional view through the spinal cord and meninges, showing the peripheral distribution of spinal nerves. 1
regulate spinal reflexes. Receipt of sensory impulses may activity, smooth muscle activity and secretion by both
cause a reaction anywhere in the body; alternatively, the endocrine and exocrine glands.
signal might be stored in the memory to be used at
some stage in the future. Within the motor division of Sensory neurons from all over the skin, except for the skin
the nervous system the spinal cord helps to control of the face and scalp, feed information into the spinal
the various bodily activities, including skeletal muscle cord through the spinal nerves. The skin surface can