Page 515 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 515
492 P R I N C I P L E S A N D P R A C T I C E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
Replacement
CVVH
CVVH
fluids
R.O K +
Blood Tap
Pump –
water HCO 3
Membrane Blood
pump
Pre & Post
Waste = Qdf + UF
Filtrate Heater
IHD
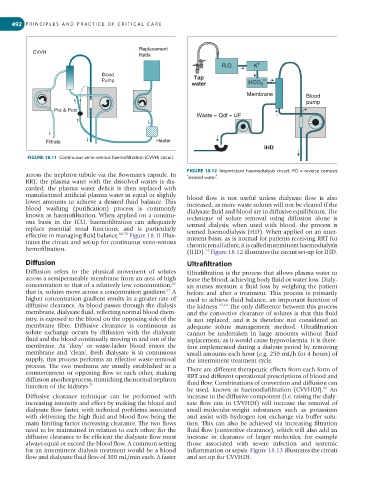
FIGURE 18.11 Continuous veno-venous haemofiltration (CVVH) circuit.
FIGURE 18.12 Intermittent haemodialysis circuit. RO = reverse osmosis
across the nephron tubule via the Bowman’s capsule. In
RRT, the plasma water with the dissolved wastes is dis- ‘treated water’.
carded; the plasma water deficit is then replaced with
manufactured artificial plasma water in equal or slightly blood flow is not useful unless dialysate flow is also
lower amounts to achieve a desired fluid balance. This increased, as more waste solutes will not be cleared if the
blood washing (purification) process is commonly dialysate fluid and blood are in diffusive equilibrium. The
known as haemofiltration. When applied on a continu- technique of solute removal using diffusion alone is
ous basis in the ICU, haemofiltration can adequately termed dialysis; when used with blood, the process is
replace essential renal functions, and is particularly termed haemodialysis (HD). When applied on an inter-
effective in managing fluid balance. 66-70 Figure 18.11 illus- mittent basis, as is normal for patients receiving RRT for
trates the circuit and set-up for continuous veno-venous chronic renal failure, it is called intermittent haemodialysis
hemofiltration.
72
(IHD). Figure 18.12 illustrates the circuit set-up for IHD.
Diffusion Ultrafiltration
Diffusion refers to the physical movement of solutes Ultrafiltration is the process that allows plasma water to
across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high leave the blood, achieving body fluid or water loss. Dialy-
concentration to that of a relatively low concentration; sis nurses measure a fluid loss by weighing the patient
66
71
that is, solutes move across a concentration gradient. A before and after a treatment. This process is primarily
higher concentration gradient results in a greater rate of used to achieve fluid balance, an important function of
diffusive clearance. As blood passes through the dialysis the kidneys. 33,66 The only difference between this process
membrane, dialysate fluid, reflecting normal blood chem- and the convective clearance of solutes is that this fluid
istry, is exposed to the blood on the opposing side of the is not replaced, and it is therefore not considered an
membrane fibre. Diffusive clearance is continuous as adequate solute management method. Ultrafiltration
solute exchange occurs by diffusion with the dialysate cannot be undertaken in large amounts without fluid
fluid and the blood continually moving in and out of the replacement, as it would cause hypovolaemia. It is there-
membrane. As ‘dirty’ or waste-laden blood enters the fore implemented during a dialysis period by removing
membrane and ‘clean’, fresh dialysate is in continuous small amounts each hour (e.g. 250 mL/h for 4 hours) of
supply, this process performs an effective waste-removal the intermittent treatment cycle.
process. The two mediums are usually established in a
countercurrent or opposing flow to each other, making There are different therapeutic effects from each form of
diffusion another process, mimicking the normal nephron RRT and different operational prescriptions of blood and
function of the kidneys. 71 fluid flow. Combinations of convection and diffusion can
66
be used, known as haemodiafiltration (CVVHDf). An
Diffusive clearance technique can be performed with increase in the diffusive component (i.e. raising the dialy-
increasing intensity and effect by making the blood and sate flow rate in CVVHDf) will increase the removal of
dialysate flow faster, with technical problems associated small-molecular-weight substances such as potassium
with delivering the high fluid and blood flow being the and assist with hydrogen ion exchange via buffer solu-
main limiting factor increasing clearance. The two flows tion. This can also be achieved via increasing filtration
need to be maintained in relation to each other; for the fluid flow (convective clearance), which will also add an
diffusive clearance to be efficient the dialysate flow must increase in clearance of larger molecules, for example
always equal or exceed the blood flow. A common setting those associated with severe infection and systemic
for an intermittent dialysis treatment would be a blood inflammation or sepsis. Figure 18.13 illustrates the circuit
flow and dialysate fluid flow of 300 mL/min each. A faster and set-up for CVVHDf.