Page 1188 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1188
1036 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
+
CD19 gate
hematogones B-ALL at diagnosis Minimal residual disease
CD20
A CD10
B
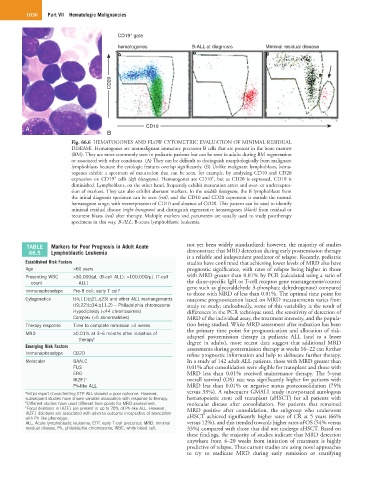
Fig. 66.6 HEMATOGONES AND FLOW CYTOMETRIC EVALUATION OF MINIMAL RESIDUAL
DISEASE. Hematogones are nonmalignant immature precursor B cells that are present in the bone marrow
(BM). They are more commonly seen in pediatric patients but can be seen in adults during BM regeneration
or associated with other conditions. (A) They can be difficult to distinguish morphologically from malignant
lymphoblasts because the cytologic features overlap significantly. (B) Unlike malignant lymphoblasts, hema-
togones exhibit a spectrum of maturation that can be seen, for example, by analyzing CD10 and CD20
+
+
expression on CD19 cells (left histogram). Hematogones are CD10 , but as CD20 is expressed, CD10 is
diminished. Lymphoblasts, on the other hand, frequently exhibit maturation arrest and over- or underexpres-
sion of markers. They can also exhibit aberrant markers. In the middle histogram, the B lymphoblasts from
the initial diagnosis specimen can be seen (red), and the CD10 and CD20 expression is outside the normal
hematogone range, with overexpression of CD10 and absence of CD20. This pattern can be used to identify
minimal residual disease (right histogram) and distinguish regenerative hematogones (black) from residual or
recurrent blasts (red) after therapy. Multiple markers and parameters are usually used to study posttherapy
specimens in this way. B-ALL, B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
TABLE Markers for Poor Prognosis in Adult Acute not yet been widely standardized; however, the majority of studies
66.5 Lymphoblastic Leukemia demonstrate that MRD detection during early postremission therapy
is a reliable and independent predictor of relapse. Recently, pediatric
Established Risk Factors studies have confirmed that achieving lower levels of MRD also have
Age >60 years prognostic significance, with rates of relapse being higher in those
Presenting WBC >30,000/µL (B-cell ALL); >100,000/µL (T-cell with MRD greater than 0.01% by PCR (calculated using a ratio of
count ALL) the clone-specific IgH or T-cell receptor gene rearrangement/control
gene such as glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase) compared
Immunophenotype Pro-B cell; early T cell a
to those with MRD of less than 0.01%. The optimal time point for
Cytogenetics t(4;11)(q21;q23) and other MLL rearrangements outcome prognostication based on MRD measurements varies from
t(9;22)(q34;q11.2) – Philadelphia chromosome study to study; undoubtedly, some of this variability is the result of
Hypodiploidy (<44 chromosomes) differences in the PCR technique used, the sensitivity of detection of
Complex (>5 abnormalities) MRD of the individual assay, the treatment intensity, and the popula-
Therapy response Time to complete remission >4 weeks tion being studied. While MRD assessment after induction has been
the primary time point for prognostication and allocation of risk-
MRD ≥0.01% at 3–6 months after initiation of adapted postremission therapy in pediatric ALL (and to a lesser
therapy b degree in adults), more recent data suggest that additional MRD
Emerging Risk Factors assessments during postremission therapy at weeks 16–22 can further
Immunophenotype CD20 refine prognostic information and help to delineate further therapy.
Molecular BAALC In a study of 142 adult ALL patients, those with MRD greater than
FUS 0.01% after consolidation were eligible for transplant and those with
ERG MRD less than 0.01% received maintenance therapy. The 5-year
IKZF1 c overall survival (OS) rate was significantly higher for patients with
Ph-like ALL MRD less than 0.01% or negative status postconsolidation (75%
a Initial report characterizing ETP ALL showed a poor outcome. However, versus 33%). A subsequent GMALL study incorporated autologous
subsequent studies have shown variable association with response to therapy. hematopoietic stem cell transplant (aHSCT) for all patients with
b Different studies have used different time points for MRD assessment. molecular disease after consolidation. For patients that remained
c Focal deletions in IKZF1 are present in up to 70% of Ph-like ALL. However, MRD positive after consolidation, the subgroup who underwent
IKZF1 deletions are associated with adverse outcome irrespective of association aHSCT achieved significantly higher rates of CR at 5 years (66%
with Ph-like phenotype.
ALL, Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; ETP, early T-cell precursor; MRD, minimal versus 12%), and this trended towards higher rates of OS (54% versus
residual disease; Ph, philadelphia chromosome; WBC, white blood cell. 33%) compared with those that did not undergo aHSCT. Based on
these findings, the majority of studies indicate that MRD detection
anywhere from 4–20 weeks from initiation of treatment is highly
predictive of relapse. Thus current studies are using novel approaches
to try to eradicate MRD during early remission or stratifying