Page 1567 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1567
1394 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
identified those patients who achieve complete molecular remissions also adequate for diagnosis (Fig. 86.7). Cytogenetic and FISH studies
that are associated with improved overall outcome. should be performed on bone marrow samples at the time of diag-
nosis, and if initially confirmed as low-risk disease, then they should
be repeated on bone marrow performed at the time of relapse.
Serum Free Light Chains Although important for prognostication, cytogenetic or FISH study–
identified abnormalities are not adequate for differentiating MM
This test measures serum light chains that are not associated with from MGUS or SMM. A seven-color flow cytometry panel is now
heavy chains. The presence of serum free light chains provides an also used with bone marrow samples to detect MRD.
additional marker and measurement of plasma cell proliferation, and
its quantitation has been used to determine protein levels in a number
of patients who were previously considered oligosecretory or nonse- Investigation to Detect End-Organ Damage
cretory. For example, 80% of patients with previously diagnosed
nonsecretory myeloma have measurable serum free light chains. The diagnosis of a plasma cell disorder is based on the presence of a
Routine use of serum free light chain measurements is indicated for monoclonal protein and clonal plasma cells. However, the diagnosis
diagnosis, response evaluation, and prognosis. As shown in patients
with MGUS and SMM, serum free light chain ratio allows for
identification of those patients with increased likelihood of progres- TABLE
sion to symptomatic myeloma. The measurement of serum free light 86.6 Phenotypic Characterization of Plasma Cells
chain does not replace the measurement of Bence Jones proteins in
24-hour urine collection. Adhesion Molecule Normal Plasma Cells MM Cells
A recently developed heavy/light chain assay allows identification CD138 + +
and quantification of the different light chain types belonging to each
immunoglobulin class (e.g., IgAκ and IgAλ) and allows calculation CD19 + −
of ratios of monoclonal/polyclonal immunoglobulins (heavy/light CD28 − −
chain ratio). In one study, heavy/light chain assays allowed quantifica- CD38 + +
tion of monoclonal proteins not accurately measurable by SPEP or CD40 + + a
nephelometry, and the heavy/light chain ratio indicated the presence
of disease in 8 of 31 patients who achieved CR and in sequential CD45 + − b
studies indicated evolving relapse in three patients before immuno- CD27 − +
fixation became positive. The assay requires further validation before CD11a + −
wider clinical use.
CD11b − −
CD44 + +
Bone Marrow Examination CD54 + +
Except for patients with solitary plasmacytoma, the presence of clonal CD56 − +
plasma cells (>5%) is usually observed in all plasma cell disorders, CD58 − +
and malignant plasma cells can be distinguished from normal plasma LFA-1 − −/+
cells by monoclonal antibody staining and flow cytometry (Table
20
86.6). Clonal plasma cell populations comprising 10% or greater RHAMM − +
of the nucleated cells within a bone marrow aspirate or biopsy VLA-4 + +
(whichever is higher if both are done) is required to differentiate VLA-5 + +
MGUS from SMM and for MM (Table 86.1). The quantitation of a CCD40 expression is enhanced on plasma cell leukemia cells relative to
plasma cells should be performed with at least a 200-cell count, and normal plasma cells and MM cells.
confirmation of clonality is essential for diagnosis, which can be done b CD45 on immature myeloma cells.
either by immunostaining using κ/λ staining or by flow cytometry LFA-1, Lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1; MM, multiple myeloma;
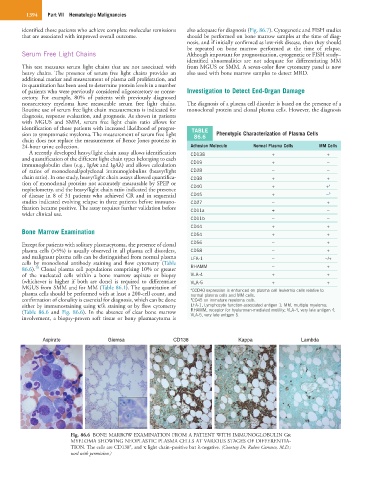
(Table 86.6 and Fig. 86.6). In the absence of clear bone marrow RHAMM, receptor for hyaluronan-mediated motility; VLA-4, very late antigen 4;
VLA-5, very late antigen 5.
involvement, a biopsy-proven soft tissue or bony plasmacytoma is
Aspirate Giemsa CD138 Kappa Lambda
Fig. 86.6 BONE MARROW EXAMINATION FROM A PATIENT WITH IMMUNOGLOBULIN Gκ
MYELOMA SHOWING NEOPLASTIC PLASMA CELLS AT VARIOUS STAGES OF DIFFERENTIA-
+
TION. The cells are CD138 , and κ light chain–positive but λ-negative. (Courtesy Dr. Ruben Carrasco, M.D.;
used with permission.)