Page 1572 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1572
Chapter 86 Plasma Cell Neoplasms 1399
1.0 1.0
Progression-free survival (probability) 0.6 Overall survival (probability) 0.6
0.8
0.8
0.4
0.4
Median PFS
Median OS
0.2 R-ISS I 66 months 0.2 R-ISS I NR
R-ISS II 42 months R-ISS II 83 months
R-ISS III 29 months R-ISS III 43 months
0 0
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 0 12 24 36 48 60 72
Time (months) Time (months)
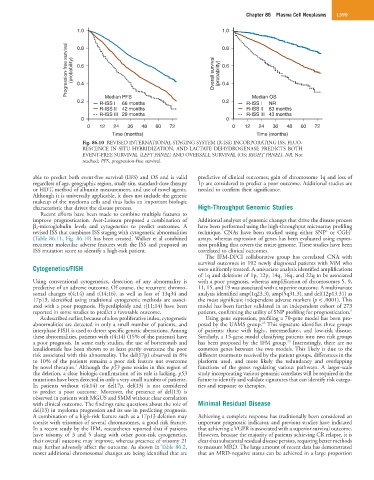
Fig. 86.10 REVISED INTERNATIONAL STAGING SYSTEM (R-ISS) INCORPORATING ISS, FLUO-
RESCENCE IN SITU HYBRIDIZATION, AND LACTATE DEHYDROGENASE PREDICTS BOTH
EVENT-FREE SURVIVAL (LEFT PANEL) AND OVERSALL SURVIVAL (OS; RIGHT PANEL). NR, Not
reached; PFS, progression-free survival.
able to predict both event-free survival (EFS) and OS and is valid predictive of clinical outcomes; gain of chromosome 1q and loss of
regardless of age, geographic region, study site, standard-dose therapy 1p are considered to predict a poor outcome. Additional studies are
or HDT, method of albumin measurement, and use of novel agents. needed to confirm their significance.
Although it is universally applicable, it does not include the genetic
makeup of the myeloma cells and thus lacks an important biologic
characteristic that drives the disease process. High-Throughput Genomic Studies
Recent efforts have been made to combine multiple features to
improve prognostication. Avet-Loiseau proposed a combination of Additional analyses of genomic changes that drive the disease process
β 2 -microglobulin levels and cytogenetics to predict outcomes. A have been performed using the high-throughput microarray profiling
7
6
revised ISS that combines ISS staging with cytogenetic abnormalities technique. CNAs have been studied using either SNP or CGH
(Table 86.11, Fig. 86.10) has been created. Walker et al combined arrays, whereas expression of genes has been evaluated using expres-
recurrent molecular adverse features with the ISS and proposed an sion profiling that covers the entire genome. These studies have been
ISS mutation score to identify a high-risk patient. correlated to clinical outcomes.
The IFM-DFCI collaborative group has correlated CNA with
survival outcomes in 192 newly diagnosed patients with MM who
Cytogenetics/FISH were uniformly treated. A univariate analysis identified amplifications
of 1q and deletions of 1p, 12p, 14q, 16q, and 22q to be associated
Using conventional cytogenetics, detection of any abnormality is with a poor prognosis, whereas amplification of chromosomes 5, 9,
predictive of an adverse outcome. Of course, the recurrent chromo- 11, 15, and 19 was associated with a superior outcome. A multivariate
somal changes t(4;14) and t(14;16), as well as loss of 13q34 and analysis identified amp(1q23.3), amp(5q31.3), and del(12p13.31) as
17p13, identified using traditional cytogenetic methods are associ- the most significant independent adverse markers (p < .0001). This
ated with a poor prognosis. Hyperdiploidy and t(11;14) have been model has been further validated in an independent cohort of 273
reported in some studies to predict a favorable outcome. patients, confirming the utility of SNP profiling for prognostication. 6
As described earlier, because of a low proliferative index, cytogenetic Using gene expression, profiling a 70-gene model has been pro-
23
abnormalities are detected in only a small number of patients, and posed by the UAMS group. This signature identifies three groups
interphase FISH is used to detect specific genetic aberrations. Among of patients: those with high-, intermediate-, and low-risk disease.
these abnormalities, patients with t(4;14) (15% of the patients) have Similarly, a 15-gene model classifying patients into two risk groups
24
a poor prognosis. In some early studies, the use of bortezomib and has been proposed by the IFM group. Interestingly, there are no
lenalidomide has been shown to at least partly overcome the poor common genes between the two models. This likely is due to the
risk associated with this abnormality. The del(17p) observed in 8% different treatments received by the patient groups, differences in the
to 10% of the patients remains a poor risk feature not overcome platform used, and more likely the redundancy and overlapping
3
by novel therapies. Although the p53 gene resides in this region of functions of the genes regulating various pathways. A larger-scale
the deletion, a clear biologic confirmation of its role is lacking. p53 study incorporating various genomic correlates will be required in the
mutations have been detected in only a very small number of patients. future to identify and validate signatures that can identify risk catego-
In patients without t(4;14) or del17p, del(13) is not considered ries and response to therapies.
to predict a poor outcome. Moreover, the presence of del(13) is
observed in patients with MGUS and SMM without clear correlation
with clinical outcome. The findings raise questions about the role of Minimal Residual Disease
del(13) in myeloma progression and its use in predicting prognosis.
A combination of a high-risk feature such as a 17p13 deletion may Achieving a complete response has traditionally been considered an
coexist with trisomies of several chromosomes, a good risk feature. important prognostic indicator, and previous studies have indicated
In a recent study by the IFM, researcheres reported that if patients that achieving a VGPR is associated with a superior survival outcome.
have trisomy of 3 and 5 along with other poor-risk cytogenetics, However, because the majority of patients achieving CR relapse, it is
their overall outcome may improve, whereas presence of trisomy 21 clear that substantial residual disease persists, requiring better methods
may further adversely affect the outcome. As shown in Table 86.2, to measure MRD. The large amount of recent data has demonstrated
newer additional chromosomal changes are being identified that are that an MRD-negative status can be achieved in a large proportion