Page 1570 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1570
Chapter 86 Plasma Cell Neoplasms 1397
lesions within the background of generalized involvement of the bone CR is a good prognostic feature and is being considered as one of the
marrow. MRI is indicated in all patients with a suspected diagnosis methods to better define a CR.
of a solitary plasmacytoma and is indicated in SMM to identify any CT has been used to evaluate focal lesions in order to perform
occult bone marrow involvement. Identification of multiple lesions fine-needle biopsies for cytologic analysis. CT scans provide a better
not observed on a skeletal survey allows prediction of progression and picture of the bone component and can also be used to judge the
early intervention. integrity of the bone. PET along with CT can be used to define
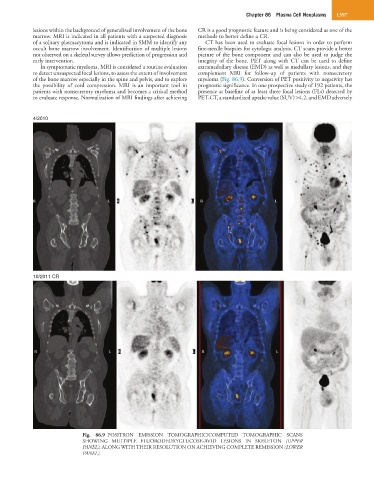
In symptomatic myeloma, MRI is considered a routine evaluation extramedullary disease (EMD) as well as medullary lesions, and they
to detect unsuspected focal lesions, to assess the extent of involvement complement MRI for follow-up of patients with nonsecretory
of the bone marrow especially in the spine and pelvis, and to explore myeloma (Fig. 86.9). Conversion of PET positivity to negativity has
the possibility of cord compression. MRI is an important tool in prognostic significance. In one prospective study of 192 patients, the
patients with nonsecretory myeloma and becomes a critical method presence at baseline of at least three focal lesions (FLs) detected by
to evaluate response. Normalization of MRI findings after achieving PET-CT, a standardized uptake value (SUV) >4.2, and EMD adversely
4/2010
10/2011 CR
Fig. 86.9 POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPHIC/COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHIC SCANS
SHOWING MULTIPLE FLUORODEOXYGLUCOSE-AVID LESIONS IN SKELETON (UPPER
PANEL), ALONG WITH THEIR RESOLUTION ON ACHIEVING COMPLETE REMISSION (LOWER
PANEL).