Page 1569 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1569
A B
D E C
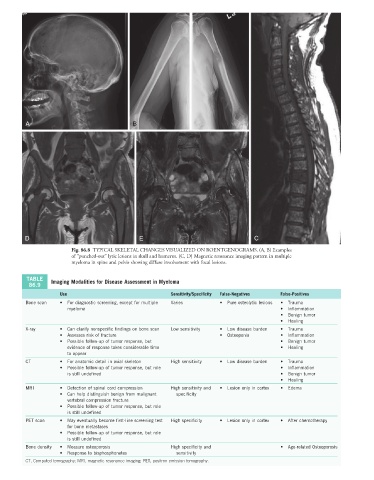
Fig. 86.8 TYPICAL SKELETAL CHANGES VISUALIZED ON ROENTGENOGRAMS. (A, B) Examples
of “punched-out” lytic lesions in skull and humerus. (C, D) Magnetic resonance imaging pattern in multiple
myeloma in spine and pelvis showing diffuse involvement with focal lesions.
TABLE Imaging Modalities for Disease Assessment in Myeloma
86.9
Use Sensitivity/Specificity False-Negatives False-Positives
Bone scan • For diagnostic screening, except for multiple Varies • Pure osteolytic lesions • Trauma
myeloma • Inflammation
• Benign tumor
• Healing
X-ray • Can clarify nonspecific findings on bone scan Low sensitivity • Low disease burden • Trauma
• Assesses risk of fracture • Osteopenia • Inflammation
• Possible follow-up of tumor response, but • Benign tumor
evidence of response takes considerable time • Healing
to appear
CT • For anatomic detail in axial skeleton High sensitivity • Low disease burden • Trauma
• Possible follow-up of tumor response, but role • Inflammation
is still undefined • Benign tumor
• Healing
MRI • Detection of spinal cord compression High sensitivity and • Lesion only in cortex • Edema
• Can help distinguish benign from malignant specificity
vertebral compression fracture
• Possible follow-up of tumor response, but role
is still undefined
PET scan • May eventually become first-line screening test High specificity • Lesion only in cortex • After chemotherapy
for bone metastases
• Possible follow-up of tumor response, but role
is still undefined
Bone density • Measure osteoporosis High specificity and • Age-related Osteoporosis
• Response to bisphosphonates sensitivity
CT, Computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; PET, positron emission tomography.