Page 1618 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1618
Chapter 88 Immunoglobulin Light Chain Amyloidosis (Primary Amyloidosis) 1439
1.0 orthostatic syncope but are associated with both fluid retention and
0.9 supine hypertension, making their use a challenge. The diarrhea
associated with GI amyloid is also challenging. It is common for these
0.8 patients to fail imodium therapy and loperamide. We frequently will
0.7 use tincture of opium to manage this. In refractory instances where
fecal incontinence is common, the placement of a diverting sigmoid
0.6
Surviving 0.5 colostomy has no impact on the diarrhea but can provide the patient
important improved quality of life and social relief.
0.4
0.3 Chemotherapy Treatment for Light Chain Amyloidosis
0.2
0.1 The chemotherapy treatment of light-chain amyloidosis requires a
0.0 determination of whether the patients are candidates for high-dose
0 50 100 therapy with stem cell transplant or are best served with conventional
chemotherapy regimens.
Survival months It is now 40 years since melphalan and prednisone treatment was
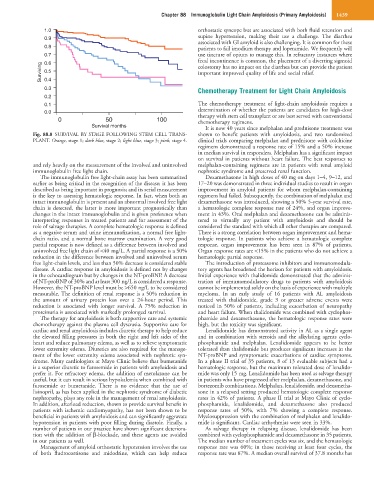
Fig. 88.8 SURVIVAL BY STAGE FOLLOWING STEM CELL TRANS- shown to benefit patients with amyloidosis, and two randomized
PLANT. Orange, stage 1; dark blue, stage 2; light blue, stage 3; pink, stage 4. clinical trials comparing melphalan and prednisone with colchicine
regimens demonstrated a response rate of 15% and a 50% increase
in median survival in responders. Melphalan has a significant impact
on survival in patients without heart failure. The best responses to
and rely heavily on the measurement of the involved and uninvolved melphalan-containing regimens are in patients with renal amyloid
immunoglobulin free light chain. nephrotic syndrome and preserved renal function.
The immunoglobulin free light-chain assay has been summarized Dexamethasone in high doses of 40 mg on days 1–4, 9–12, and
earlier as being critical in the recognition of the disease; it has been 17–20 was demonstrated in three individual studies to result in organ
described as being important in prognosis; and its serial measurement improvement in amyloid patients for whom melphalan-containing
is the key to assessing hematologic response. In fact, when both an regimens had failed. Subsequently, the combination of melphalan and
intact immunoglobulin is present and an abnormal involved free light dexamethasone was introduced, showing a 50% 5-year survival rate,
chain is detected, the latter is more important prognostically than a hematologic complete response rate of 24%, and organ improve-
changes in the intact immunoglobulin and is given preference when ment in 43%. Oral melphalan and dexamethasone can be adminis-
interpreting responses in treated patients and for assessment of the tered to virtually any patient with amyloidosis and should be
role of salvage therapies. A complete hematologic response is defined considered the standard with which all other therapies are compared.
as a negative serum and urine immunofixation, a normal free light- There is a strong correlation between organ improvement and hema-
chain ratio, and a normal bone marrow examination. A very good tologic response. In patients who achieve a hematologic complete
partial response is now defined as a difference between involved and response, organ improvement has been seen in 87% of patients.
uninvolved free light chain of <40 mg/L. A partial response is a 50% Organ response rates are <15% in the patients who do not achieve a
reduction in the difference between involved and uninvolved serum hematologic partial response.
free light-chain levels, and less than 50% decrease is considered stable The introduction of proteasome inhibitors and immunomodula-
disease. A cardiac response in amyloidosis is defined not by changes tory agents has broadened the horizon for patients with amyloidosis.
in the echocardiogram but by changes in the NT-proBNP. A decrease Initial experience with thalidomide demonstrated that the adminis-
of NT-proBNP of 30% and at least 300 ng/L is considered a response. tration of immunomodulatory drugs to patients with amyloidosis
However, the NT-proBNP level must be >650 ng/L to be considered cannot be implemented solely on the basis of experience with multiple
measurable. The definition of renal response is a 50% reduction in myeloma. In an early study of 16 patients with AL amyloidosis
the amount of urinary protein loss over a 24-hour period. This treated with thalidomide, grade 3 or greater adverse events were
reduction is associated with longer survival. A 75% reduction in noticed in 50% of patients, including exacerbation of neuropathy
proteinuria is associated with markedly prolonged survival. and heart failure. When thalidomide was combined with cyclophos-
The therapy for amyloidosis is both supportive care and systemic phamide and dexamethasone, the hematologic response rates were
chemotherapy against the plasma cell dyscrasia. Supportive care for high, but the toxicity was significant.
cardiac and renal amyloidosis includes diuretic therapy to help reduce Lenalidomide has demonstrated activity in AL as a single agent
the elevated filling pressures in both the right and left sides of the and in combination with steroids and the alkylating agents cyclo-
heart and reduce pulmonary edema, as well as to relieve symptomatic phosphamide and melphalan. Lenalidomide appears to be better
lower extremity edema. Diuretics are also required for the manage- tolerated than thalidomide but produces significant increases in the
ment of the lower extremity edema associated with nephrotic syn- NT-proBNP and symptomatic exacerbations of cardiac symptoms.
drome. Many cardiologists at Mayo Clinic believe that bumetanide In a phase II trial of 35 patients, 8 of 13 evaluable subjects had a
is a superior diuretic to furosemide in patients with amyloidosis and hematologic response, but the maximum tolerated dose of lenalido-
prefer it. For refractory edema, the addition of metolazone can be mide was only 15 mg. Lenalidomide has been used as salvage therapy
useful, but it can result in serious hypokalemia when combined with in patients who have progressed after melphalan, dexamethasone, and
furosemide or bumetanide. There is no evidence that the use of bortezomib combinations. Melphalan, lenalidomide, and dexametha-
lisinopril, as has been applied in the nephrotic syndrome of diabetic sone in a relapsed setting produced hematologic complete response
nephropathy, plays any role in the management of renal amyloidosis. rates in 42% of patients. A phase II trial at Mayo Clinic of cyclo-
In addition, afterload reduction, shown to provide survival benefit in phosphamide, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone also produced
patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy, has not been shown to be response rates of 50%, with 7% showing a complete response.
beneficial in patients with amyloidosis and can significantly aggravate Myelosuppression with the combination of melphalan and lenalido-
hypotension in patients with poor filling during diastole. Finally, a mide is significant. Cardiac arrhythmias were seen in 33%.
number of patients in our practice have shown significant deteriora- As salvage therapy in relapsing disease, lenalidomide has been
tion with the addition of β-blockade, and these agents are avoided combined with cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone in 35 patients.
in our patients as well. The median number of treatment cycles was six, and the hematologic
Management of amyloid orthostatic hypotension involves the use response rate was 60%; in those receiving at least four cycles, the
of both fludrocortisone and midodrine, which can help reduce response rate was 87%. A median overall survival of 37.8 months has