Page 1617 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1617
1438 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
50
40
Patients, No. 30
20
10
0
≤35 36–40 41–45 46–50 51–55 56–60 61–65 66–70 71–75 ≥76 Unknown
Age at Diagnosis, y age
Thr60Ala Val30Met Val122lle Ser77Tyr Other TTR Non–TTR Unknown
mutation
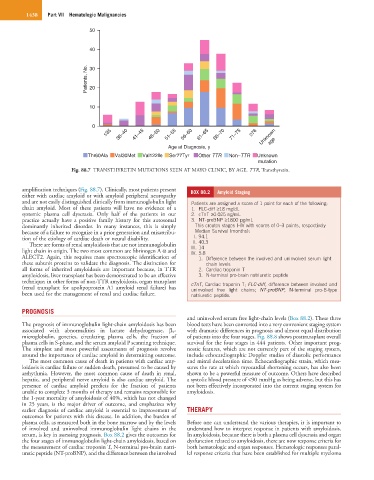
Fig. 88.7 TRANSTHYRETIN MUTATIONS SEEN AT MAYO CLINIC, BY AGE. TTR, Transthyretin.
amplification techniques (Fig. 88.7). Clinically, most patients present BOX 88.2 Amyloid Staging
either with cardiac amyloid or with amyloid peripheral neuropathy
and are not easily distinguished clinically from immunoglobulin light Patients are assigned a score of 1 point for each of the following:
chain amyloid. Most of these patients will have no evidence of a 1. FLC-diff ≥18 mg/dL
systemic plasma cell dyscrasia. Only half of the patients in our 2. cTnT ≥0.025 ng/mL
practice actually have a positive family history for this autosomal 3. NT-proBNP ≥1800 pg/mL
dominantly inherited disorder. In many instances, this is simply This creates stages I–IV with scores of 0–3 points, respectively
because of a failure to recognize in a prior generation and misattribu- Median Survival (months):
tion of the etiology of cardiac death or neural disability. I. 94.1
There are forms of renal amyloidosis that are not immunoglobulin II. 40.3
light chain in origin. The two most common are fibrinogen A α and III. 14
IV. 5.8
ALECT2. Again, this requires mass spectroscopic identification of 1. Difference between the involved and uninvolved serum light
these subunit proteins to validate the diagnosis. The distinction for chain levels
all forms of inherited amyloidosis are important because, in TTR 2. Cardiac troponin T
amyloidosis, liver transplant has been demonstrated to be an effective 3. N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide
technique; in other forms of non-TTR amyloidosis, organ transplant cTnT, Cardiac troponin T; FLC-diff, difference between involved and
(renal transplant for apolipoprotein A1 amyloid renal failure) has uninvolved free light chains; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-B-type
been used for the management of renal and cardiac failure. natriuretic peptide.
PROGNOSIS
and uninvolved serum free light-chain levels (Box 88.2). These three
The prognosis of immunoglobulin light-chain amyloidosis has been blood tests have been converted into a very convenient staging system
associated with abnormalities in lactate dehydrogenase, β 2 - with dramatic differences in prognosis and almost equal distribution
microglobulin, genetics, circulating plasma cells, the fraction of of patients into the four stages. Fig. 88.8 shows posttransplant overall
plasma cells in S-phase, and the serum amyloid P scanning technique. survival for the four stages in 444 patients. Other important prog-
The simplest and most powerful assessments of prognosis revolve nostic features, which are not currently part of the staging system,
around the importance of cardiac amyloid in determining outcome. include echocardiographic Doppler studies of diastolic performance
The most common cause of death in patients with cardiac amy- and mitral deceleration time. Echocardiographic strain, which mea-
loidosis is cardiac failure or sudden death, presumed to be caused by sures the rate at which myocardial shortening occurs, has also been
arrhythmia. However, the most common cause of death in renal, shown to be a powerful measure of outcome. Others have described
hepatic, and peripheral nerve amyloid is also cardiac amyloid. The a systolic blood pressure of <90 mmHg as being adverse, but this has
presence of cardiac amyloid predicts for the fraction of patients not been effectively incorporated into the current staging system for
unable to complete 3 months of therapy and remains responsible for amyloidosis.
the 1-year mortality of amyloidosis of 40%, which has not changed
in 25 years, is the major driver of outcome, and emphasizes why
earlier diagnosis of cardiac amyloid is essential to improvement of THERAPY
outcomes for patients with this disease. In addition, the burden of
plasma cells, as measured both in the bone marrow and by the levels Before one can understand the various therapies, it is important to
of involved and uninvolved immunoglobulin light chains in the understand how to interpret response in patients with amyloidosis.
serum, is key in assessing prognosis. Box 88.2 gives the outcomes for In amyloidosis, because there is both a plasma cell dyscrasia and organ
the four stages of immunoglobulin light-chain amyloidosis, based on dysfunction related to amyloidosis, there are now response criteria for
the measurement of cardiac troponin T, N-terminal pro-brain natri- both hematologic and organ responses. Hematologic responses paral-
uretic peptide (NT-proBNP), and the difference between the involved lel response criteria that have been established for multiple myeloma