Page 2104 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2104
Chapter 124 Megakaryocyte and Platelet Structure 1867
platelet microtubules with drugs such as vincristine, colchicine, or Actin is the most abundant of all the platelet proteins, with 2
nocodazole causes platelets to become round and to lose their discoid million molecules expressed per platelet. Of these molecules, 800,000
shape. Cooling the platelets also causes disassembly of the microtubule assemble to form the 2000–5000 linear actin polymers that exist in
coil and loss of the discoid shape. Mice lacking β 1 tubulin, the major the resting cell (see Fig. 124.9A). The remainder of the actin is
hematopoietic β-tubulin isoform, produce platelets that lack their maintained in storage as a 1 : 1 complex with β 4 thymosin, which can
characteristic discoid shapes and have defective marginal bands. be converted to filaments during platelet activation to drive cell
Genetic elimination of β 1 tubulin in mice results in thrombocytopenia spreading. All evidence indicates that the filaments of the resting
with circulating platelet counts below 50% of normal. β 1 -Tubulin– platelet are interconnected at various points into a rigid cytoplasmic
deficient platelets are spherical in shape, apparently due to shortened network because platelets express high concentrations of actin cross-
7
marginal bands with fewer coilings. Whereas normal platelets possess linking proteins, including filamin and α-actinin. Both filamin and
a marginal band that consists of 8–12 coils, β 1 -tubulin knockout α-actinin are homodimers in solution. Three filamin genes are located
platelets contain only 2–3 coils. A human β 1-tubulin functional on chromosomes 3, 7, and X. Filamin A (X) and filamin B (3) are
substitution (AG→CC) inducing both structural and functional expressed in platelets. Filamin A is expressed at levels more than
platelet alterations has been described. Of note, the Q43P β 1-tubulin 10-fold higher than that of filamin B. Filamin subunits are elongated
variant was found in 10.6% of the general population and in 24.2% strands composed primarily of 24 repeats, each approximately 100
of 33 unrelated patients with undefined congenital macrothrombo- amino acids in length and folded into immunoglobulin G-like
cytopenia. Electron microscopy revealed enlarged spherocytic platelets β-barrels. Each strand has an N-terminus actin-binding site that
with a disrupted marginal band and structural alterations. Platelets shares homology with other actin-binding proteins, two rod domains
with the Q43P β 1-tubulin variant showed mild platelet dysfunction that are end-to-end assemblies of the repeat units, interrupted by two
with reduced ATP secretion, attenuated thrombin receptor-activating hinge domains between repeats 15 and 16, and 23 and 24, and a
peptide (TRAP)–induced aggregation, and impaired adhesion to C-terminus self-association site (Fig. 124.10B). Subunits assemble to
25
collagen under flow conditions. A more-than-doubled prevalence form V-shaped bipolar molecules—that is, the self-association site is
of the β 1 -tubulin variant was observed in healthy subjects not under- the vertex of the V, and the actin-binding sites are on the free ends.
going ischemic events, raising the possibility that the variant confers Inclusion of the first hinge in filamin depends on alternative RNA
an evolutionary advantage and a protective cardiovascular role. splicing. Filamin now is recognized to be a prototype “scaffolding
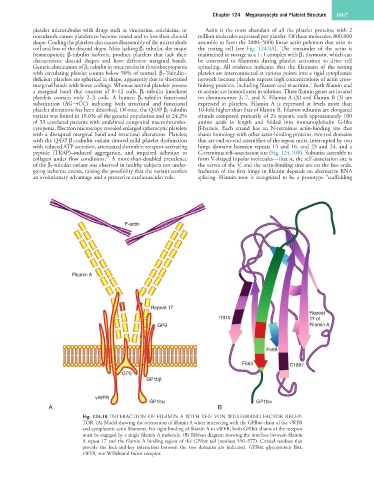
F-actin
Filamin A
Repeat 17
Repeat
11910 17 of
GP9 Filamin A
F568
F563 C1897
GP5
GP1bβ
vWFR
GP1bα GP1bα
A B
Fig. 124.10 INTERACTION OF FILAMIN A WITH THE VON WILLEBRAND FACTOR RECEP-
TOR. (A) Model showing the orientation of filamin A when interacting with the GPIbα chain of the vWFR
and cytoplasmic actin filaments. For tight binding of filamin A to vWFR, both GPIbα chains of the receptor
must be engaged by a single filamin A molecule. (B) Ribbon diagram showing the interface between filamin
A repeat 17 and the filamin A binding region of the GPIbα tail (residues 556–577). Critical residues that
provide the lock-and-key interaction between the two domains are indicated. GPIbα, glycoprotein Ibα;
vWFR, von Willebrand factor receptor.