Page 2127 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2127
1888 Part XII Hemostasis and Thrombosis
R152 – I153
FACTOR VII
NH 2 Gla EGF1 EGF2 Serine protease COOH
S S
R145 – A146 R180 – V181
FACTOR IX
NH 2 Gla EGF1 EGF2 AP Serine protease COOH
S S
R194 – I195
FACTOR X
NH 2 Gla EGF1 EGF2 AP Serine protease COOH
S S
R271 – T272 R320 – I321
PROTHROMBIN
NH 2 Gla K1 K2 Serine protease COOH
S S
R169 – L170
PROTEIN C
NH 2 Gla EGF1 EGF2 AP Serine protease COOH
S S
PROTEIN S
NH 2 Gla TSR EGF1 EGF2 EGF3 EGF4 SHGB domain COOH
PROTEIN Z
NH 2 Gla EGF1 EGF2 Pseudo catalytic domain COOH
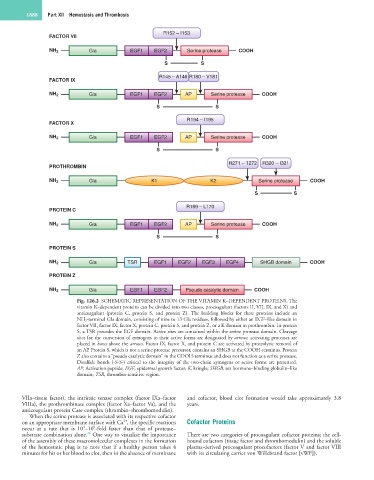
Fig. 126.2 SCHEMATIC REPRESENTATION OF THE VITAMIN K–DEPENDENT PROTEINS. The
vitamin K–dependent proteins can be divided into two classes, procoagulant (factors II, VII, IX, and X) and
anticoagulant (protein C, protein S, and protein Z). The building blocks for these proteins include an
NH 2-terminal Gla domain, consisting of nine to 13 Gla residues, followed by either an EGF–like domain in
factor VII, factor IX, factor X, protein C, protein S, and protein Z, or a K domain in prothrombin. In protein
S, a TSR precedes the EGF domain. Active sites are contained within the serine protease domain. Cleavage
sites for the conversion of zymogens to their active forms are designated by arrows; activating proteases are
placed in boxes above the arrows. Factor IX, factor X, and protein C are activated by proteolytic removal of
an AP. Protein S, which is not a serine protease precursor, contains an SHGB at the COOH-terminus. Protein
Z also contains a “pseudo catalytic domain” in the COOH-terminus and does not function as a serine protease.
Disulfide bonds (-S-S-) critical to the integrity of the two-chain zymogens or active forms are presented.
AP, Activation peptide; EGF, epidermal growth factor; K, kringle; SHGB, sex hormone–binding globulin–like
domain; TSR, thrombin-sensitive region.
VIIa–tissue factor), the intrinsic tenase complex (factor IXa–factor and cofactor, blood clot formation would take approximately 3.8
VIIIa), the prothrombinase complex (factor Xa–factor Va), and the years.
anticoagulant protein Case complex (thrombin–thrombomodulin).
When the serine protease is associated with its respective cofactor
2+
on an appropriate membrane surface with Ca , the specific reactions Cofactor Proteins
9
4
occur at a rate that is 10 –10 -fold faster than that of protease–
26
substrate combination alone. One way to visualize the importance There are two categories of procoagulant cofactor proteins; the cell-
of the assembly of these macromolecular complexes in the formation bound cofactors (tissue factor and thrombomodulin) and the soluble
of the hemostatic plug is to note that if a healthy person takes 4 plasma-derived procoagulant procofactors (factor V and factor VIII
minutes for his or her blood to clot, then in the absence of membrane with its circulating carrier von Willebrand factor [vWF]).