Page 519 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 519
Chapter 32 Acquired Disorders of Red Cell, White Cell, and Platelet Production 439
cyclophosphamide was 64% following initial methotrexate therapy. cell junctions into the lumen of marrow capillaries. The pseudopods
Therapy with cyclophosphamide in neutropenic patients may be fracture, because of shear stress in the lumen of these capillaries, and
difficult because of myelosuppression. In most refractory cases, ATG release shards of megakaryocytic cytoplasm, or proplatelets, that are
has also been used with success. In recent years, successful therapy the immediate antecedents of circulating platelets. A fully mature
3
with alemtuzumab has been reported. CD52 expression determined megakaryocyte is estimated to produce approximately 1–1.5 × 10
by flow cytometry is an important predictive factor for response to platelets. The molecular regulation of this process is beginning to be
alemtuzumab. High response rates with the Janus-activated kinase better understood. It has been shown, for example, that the apoptosis-
inhibitor, tofacitinib citrate have been observed (66%) when used as stimulating gene Bax promotes platelet production. Interestingly,
a salvage therapy. Currently such a therapy is approved in cases of very recent evidence suggests that the life span of circulating platelets
LGL with rheumatoid arthritis. Purine analogues like fludarabine is also regulated by the apoptosis proteins. Using the strategy of
222
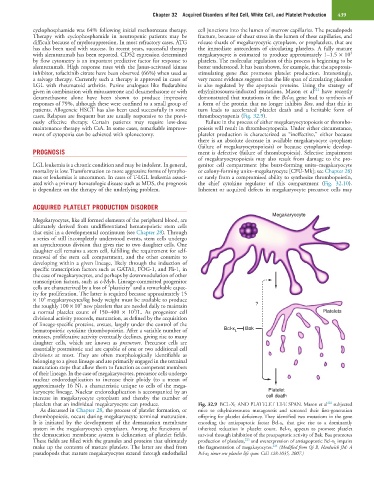
given in combination with mitoxantrone and dexamethasone or with ethylnitrosourea-inducted mutations, Mason et al have recently
dexamethasone alone have been shown to produce impressive demonstrated that mutations in the Bcl-x L gene lead to synthesis of
responses of 79%, although these were confined to a small group of a form of the protein that no longer inhibits Bax, and that this in
patients. Allogeneic HSCT has also been used successfully in some turn leads to accelerated platelet death and a heritable form of
cases. Relapses are frequent but are usually responsive to the previ- thrombocytopenia (Fig. 32.9).
ously effective therapy. Certain patients may require low-dose Failure in the process of either megakaryocytopoiesis or thrombo-
maintenance therapy with CsA. In some cases, remarkable improve- poiesis will result in thrombocytopenia. Under either circumstance,
ment of cytopenia can be achieved with splenectomy. platelet production is characterized as “ineffective,” either because
there is an absolute decrease in available megakaryocyte cytoplasm
(failure of megakaryocytopoiesis) or because cytoplasmic develop-
PROGNOSIS ment is defective (failure of thrombopoiesis). Selective impairment
of megakaryocytopoiesis may also result from damage to the pro-
LGL leukemia is a chronic condition and may be indolent. In general, genitor cell compartment (the burst-forming units–megakaryocyte
mortality is low. Transformation to more aggressive forms of lympho- or colony-forming units–megakaryocyte [CFU-Mk]; see Chapter 28)
mas or leukemias is uncommon. In cases of T-LGL leukemia associ- or rarely from a compromised ability to synthesize thrombopoietin,
ated with a primary hematologic disease such as MDS, the prognosis the chief cytokine regulator of this compartment (Fig. 32.10).
is dependent on the therapy of the underlying problem. Inherent or acquired defects in megakaryocyte precursor cells may
ACQUIRED PLATELET PRODUCTION DISORDER
Megakaryocyte
Megakaryocytes, like all formed elements of the peripheral blood, are
ultimately derived from undifferentiated hematopoietic stem cells
that exist in a developmental continuum (see Chapter 28). Through
a series of still incompletely understood events, stem cells undergo
an asynchronous division that gives rise to two daughter cells. One
daughter cell remains a stem cell, fulfilling the requirement for self-
renewal of the stem cell compartment, and the other commits to
developing within a given lineage, likely through the induction of
specific transcription factors such as GATA1, FOG-1, and Fli-1, in
the case of megakaryocytes, and perhaps by downmodulation of other
transcription factors, such as c-Myb. Lineage-committed progenitor
cells are characterized by a loss of “plasticity” and a remarkable capac-
ity for proliferation. The latter is required because approximately 15
6
× 10 megakaryocytes/kg body weight must be available to produce
9
the roughly 100 × 10 new platelets that are needed daily to maintain ?
9
a normal platelet count of 150–400 × 10 /L. As progenitor cell Platelets
divisional activity proceeds, maturation, as defined by the acquisition
of lineage-specific proteins, ensues, largely under the control of the
hematopoietic cytokine thrombopoietin. After a variable number of Bcl-x L Bak
mitoses, proliferative activity eventually declines, giving rise to many
daughter cells, which are known as precursors. Precursor cells are
essentially postmitotic and are capable of one or two additional cell
divisions at most. They are often morphologically identifiable as
belonging to a given lineage and are primarily engaged in the terminal
maturation steps that allow them to function as competent members
of their lineage. In the case of megakaryocytes, precursor cells undergo
nuclear endoreduplication to increase their ploidy (to a mean of
approximately 16 N), a characteristic unique to cells of the mega-
karyocyte lineage. Nuclear endoreduplication is accompanied by an Platelet
increase in megakaryocyte cytoplasm and thereby the number of cell death
platelets that an individual megakaryocyte can produce. Fig. 32.9 BCL-X L AND PLATELET LIFE SPAN. Mason et al subjected
222
As discussed in Chapter 28, the process of platelet formation, or mice to ethylnitrosourea mutagenesis and screened their first-generation
thrombopoiesis, occurs during megakaryocyte terminal maturation. offspring for platelet deficiency. They identified two mutations in the gene
It is initiated by the development of the demarcation membrane encoding the antiapoptotic factor Bcl-x L that give rise to a dominantly
system in the megakaryocyte’s cytoplasm. Among the functions of inherited reduction in platelet count. Bcl-x L appears to promote platelet
the demarcation membrane system is delineation of platelet fields. survival through inhibition of the proapoptotic activity of Bak. Bax promotes
These fields are filled with the granules and proteins that ultimately production of platelets, and overexpression of antiapoptotic Bcl-x L impairs
223
make up the contents of mature platelets. The latter are shed from the fragmentation of megakayocytes. (Modified from Qi B, Hardwick JM: A
224
pseudopods that mature megakaryocytes extend through endothelial Bcl-x L timer sets platelet life span. Cell 128:1035, 2007.)