Page 517 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 517
Chapter 32 Acquired Disorders of Red Cell, White Cell, and Platelet Production 437
CD8 Gate
ECD
CD4 Gate
PCP
CD4 Gate CD8 Gate
VB13.1 FITC
FITC VB13.2 FITC/PE
VB13.3 PE
PE
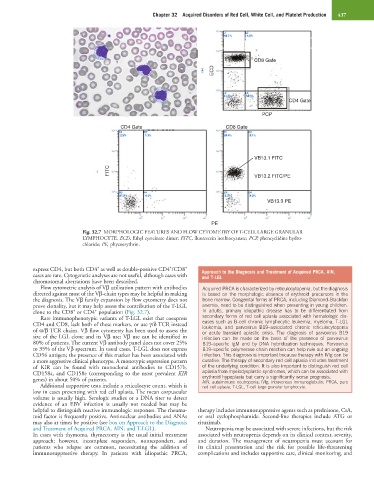
Fig. 32.7 MORPHOLOGIC FEATURES AND FLOW CYTOMETRY OF T-CELL LARGE GRANULAR
LYMPHOCYTE. ECD, Ethyl cysteinate dimer; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; PCP, phencyclidine hydro-
chloride; PE, phycoerythrin.
+
+
+
express CD4, but both CD4 as well as double-positive CD4 /CD8 Approach to the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acquired PRCA, AIN,
cases are rare. Cytogenetic analyses are not useful, although cases with and T-LGL
chromosomal aberrations have been described.
Flow cytometric analysis of Vβ utilization pattern with antibodies Acquired PRCA is characterized by reticulocytopenia, but the diagnosis
directed against most of the Vβ-chain types may be helpful in making is based on the morphologic absence of erythroid precursors in the
the diagnosis. The Vβ family expansion by flow cytometry does not bone marrow. Congenital forms of PRCA, including Diamond-Blackfan
prove clonality, but it may help assess the contribution of the T-LGL anemia, need to be distinguished when presenting in young children.
+
+
clone to the CD8 or CD4 population (Fig. 32.7). In adults, primary idiopathic disease has to be differentiated from
Rare immunophenotypic variants of T-LGL exist that coexpress secondary forms of red cell aplasia associated with hematologic dis-
CD4 and CD8, lack both of these markers, or use γ/δ TCR instead eases such as B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia, myeloma, T-LGL
leukemia, and parvovirus B19–associated chronic reticulocytopenia
of α/β TCR chains. Vβ flow cytometry has been used to assess the or acute transient aplastic crisis. The diagnosis of parvovirus B19
size of the LGL clone and its Vβ use; Vβ use can be identified in infection can be made on the basis of the presence of parvovirus
80% of patients. The current Vβ antibody panel does not cover 25% B19–specific IgM and by DNA hybridization techniques. Parvovirus
to 35% of the Vβ spectrum. In usual cases, T-LGL does not express B19–specific polymerase chain reaction can help rule out an ongoing
CD56 antigen; the presence of this marker has been associated with infection. This diagnosis is important because therapy with IVIg can be
a more aggressive clinical phenotype. A monotypic expression pattern curative. The therapy of secondary red cell aplasia includes treatment
of KIR can be found with monoclonal antibodies to CD157b, of the underlying condition. It is also important to distinguish red cell
CD158a, and CD158e (corresponding to the most prevalent KIR aplasia from myelodysplastic syndromes, which can be associated with
genes) in about 50% of patients. erythroid hypoplasia but carry a significantly worse prognosis.
AIN, autoimmune neutropenia; IVIg, intravenous immunoglobulin; PRCA, pure
Additional supportive tests include a reticulocyte count, which is red cell aplasia; T-LGL, T-cell large granular lymphocyte.
low in cases presenting with red cell aplasia. The mean corpuscular
volume is usually high. Serologic studies or a DNA titer to detect
evidence of an EBV infection is usually not needed but may be
helpful to distinguish reactive immunologic responses. The rheuma- therapy includes immunosuppressive agents such as prednisone, CsA,
toid factor is frequently positive. Antinuclear antibodies and ANAs or oral cyclophosphamide. Second-line therapies include ATG or
may also at times be positive (see box on Approach to the Diagnosis rituximab.
and Treatment of Acquired PRCA, AIN, and T-LGL). Neutropenia may be associated with severe infections, but the risk
In cases with thymoma, thymectomy is the usual initial treatment associated with neutropenia depends on its clinical context, severity,
approach; however, incomplete responders, nonresponders, and and duration. The management of neutropenia must account for
patients who relapse are common, necessitating the addition of its clinical presentation and the risk for possible life-threatening
immunosuppressive therapy. In patients with idiopathic PRCA, complications and includes supportive care, clinical monitoring, and