Page 555 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 555
470 Part V Red Blood Cells
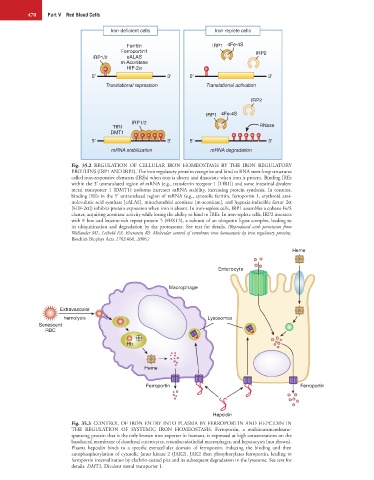
Iron-deficient cells Iron-replete cells
Ferritin IRP1 4Fe-4S
Ferroportin1 IRP2
IRP1/2 eALAS
m-Aconitase
HIF-2α
5 3 5 3
Translational repression Translational activation
IRP2
IRP1 4Fe-4S
IRP1/2
TfRI RNase
DMT1
5 3 5 3
mRNA stabilization mRNA degradation
Fig. 35.2 REGULATION OF CELLULAR IRON HOMEOSTASIS BY THE IRON REGULATORY
PROTEINS (IRP1 AND IRP2). The iron regulatory proteins recognize and bind to RNA stem-loop structures
called iron-responsive elements (IREs) when iron is absent and dissociate when iron is present. Binding IREs
within the 3′ untranslated region of mRNA (e.g., transferrin receptor 1 [TfR1]) and some intestinal divalent
metal transporter 1 (DMT1) isoforms increases mRNA stability, increasing protein synthesis. In contrast,
binding IREs in the 5′ untranslated region of mRNA (e.g., cytosolic ferritin, ferroportin 1, erythroid ami-
nolevulinic acid synthase [eALAS], mitochondrial aconitase [m-aconitase], and hypoxia-inducible factor 2α
[HIF-2α]) inhibits protein expression when iron is absent. In iron-replete cells, IRP1 assembles a cubane Fe/S
cluster, acquiring aconitase activity while losing the ability to bind to IREs. In iron-replete cells, IRP2 interacts
with F box and leucine-rich repeat protein 5 (FBXL5), a subunit of an ubiquitin ligase complex, leading to
its ubiquitination and degradation by the proteasome. See text for details. (Reproduced with permission from
Wallander ML, Leibold EA, Eisenstein RS: Molecular control of vertebrate iron homeostasis by iron regulatory proteins.
Biochim Biophys Acta 1763:668, 2006.)
Heme
Enterocyte
Macrophage
Extravascular
hemolysis Lysosomes
Senescent
RBC
Hb
Heme
Ferroportin Ferroportin
Hepcidin
Fig. 35.3 CONTROL OF IRON ENTRY INTO PLASMA BY FERROPORTIN AND HEPCIDIN IN
THE REGULATION OF SYSTEMIC IRON HOMEOSTASIS. Ferroportin, a multitransmembrane-
spanning protein that is the only known iron exporter in humans, is expressed at high concentrations on the
basolateral membrane of duodenal enterocytes, reticuloendothelial macrophages, and hepatocytes (not shown).
Plasma hepcidin binds to a specific extracellular domain of ferroportin, inducing the binding and then
autophosphorylation of cytosolic Janus kinase 2 (JAK2). JAK2 then phosphorylates ferroportin, leading to
ferroportin internalization by clathrin-coated pits and its subsequent degradation in the lysosome. See text for
details. DMT1, Divalent metal transporter 1.