Page 615 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 615
524 Part V Red Blood Cells
A B C
D
E F
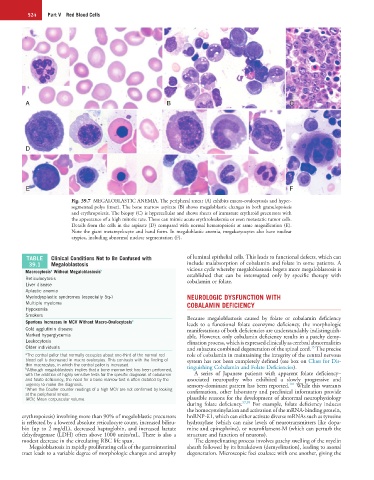
Fig. 39.7 MEGALOBLASTIC ANEMIA. The peripheral smear (A) exhibits macro-ovalocytosis and hyper-
segmented polys (inset). The bone marrow aspirate (B) shows megaloblastic changes in both granulopoiesis
and erythropoiesis. The biopsy (C) is hypercellular and shows sheets of immature erythroid precursors with
the appearance of a high mitotic rate. These can mimic acute erythroleukemia or even metastatic tumor cells.
Details from the cells in the aspirate (D) compared with normal hematopoiesis at same magnification (E).
Note the giant metamyelocyte and band form. In megaloblastic anemia, megakaryocytes also have nuclear
atypica, including abnormal nuclear segmentation (F).
TABLE Clinical Conditions Not to Be Confused with of luminal epithelial cells. This leads to functional defects, which can
39.1 Megaloblastosis include malabsorption of cobalamin and folate in some patients. A
a
Macrocytosis Without Megaloblastosis b vicious cycle whereby megaloblastosis begets more megaloblastosis is
established that can be interrupted only by specific therapy with
Reticulocytosis cobalamin or folate.
Liver disease
Aplastic anemia
Myelodysplastic syndromes (especially 5q-) NEUROLOGIC DYSFUNCTION WITH
Multiple myeloma COBALAMIN DEFICIENCY
Hypoxemia
Smokers Because megaloblastosis caused by folate or cobalamin deficiency
Spurious Increases in MCV Without Macro-Ovalocytosis c leads to a functional folate coenzyme deficiency, the morphologic
Cold agglutinin disease manifestations of both deficiencies are understandably indistinguish-
Marked hyperglycemia able. However, only cobalamin deficiency results in a patchy demy-
Leukocytosis elination process, which is expressed clinically as cerebral abnormalities
Older individuals and subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord. The precise
15
a The central pallor that normally occupies about one-third of the normal red role of cobalamin in maintaining the integrity of the central nervous
blood cell is decreased in macro-ovalocytes. This contrasts with the finding of system has not been completely defined (see box on Clues for Dis-
thin macrocytes, in which the central pallor is increased.
b Although megaloblastosis implies that a bone marrow test has been performed, tinguishing Cobalamin and Folate Deficiencies).
with the addition of highly sensitive tests for the specific diagnosis of cobalamin A series of Japanese patients with apparent folate deficiency–
and folate deficiency, the need for a bone marrow test is often dictated by the associated neuropathy who exhibited a slowly progressive and
101
urgency to make the diagnosis. sensory-dominant pattern has been reported. While this warrants
c When the Coulter counter readings of a high MCV are not confirmed by looking
at the peripheral smear. confirmation, other laboratory and preclinical information provide
MCV, Mean corpuscular volume. plausible reasons for the development of abnormal neurophysiology
during folate deficiency. 57,59 For example, folate deficiency induces
the homocysteinylation and activation of the mRNA-binding protein,
erythropoiesis) involving more than 90% of megaloblastic precursors hnRNP-E1, which can either activate diverse mRNAs such as tyrosine
is reflected by a lowered absolute reticulocyte count, increased biliru- hydroxylase (which can raise levels of neurotransmitters like dopa-
bin (up to 2 mg/dL), decreased haptoglobin, and increased lactate mine and epinephrine), or neurofilament-M (which can perturb the
dehydrogenase (LDH) often above 1000 units/mL. There is also a structure and function of neurons).
modest decrease in the circulating RBC life span. The demyelinating process involves patchy swelling of the myelin
Megaloblastosis in rapidly proliferating cells of the gastrointestinal sheath followed by its breakdown (demyelination), leading to axonal
tract leads to a variable degree of morphologic changes and atrophy degeneration. Microscopic foci coalesce with one another, giving the