Page 611 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 611
520 Part V Red Blood Cells
1. Dihydrofolate reductase
Extracellular space 2. Folylpolyglutamate synthetase
2 3 4 3. Serine hydroxymethyltransferase
1 5 4. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
H + H +
H + 5. Methionine synthetase
H + H + 6. 6/6a. Formimino transferase-cyclodeaminase
7. Formyltransferase
8. Formyl-tetrahydrofolate synthetase
Caveolae Cytoplasm
9. 8-amino-4-imidazole carboxamide
ribonucleotide (AICAR) transformylase
Receptor PteGlu 10. Formyl-tetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase
Folate 11. Glycinamide ribonucleotide (GAR)
Folate polyglutamate NADPH 1 DHFR transformylase
Channel NADP
H Proton H PteGlu 12. Methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase
+
2
Polyglutamation 13. Thymidylate synthetase
2 NADPH 1 DHFR
Homocysteine Methionine 14. Methenyltetrahydrofolate synthetase
DNA dTMP 5 NADP 15. Methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydorolase
13 TS 5–CH H PteGlu n H PteGlu n
4
3
4
dUMP methyl MS ATP
MeCbl glu 2 glu
FAD ADP
NADP
4 H PteGlu
FADH Serine 4 n FAICAR
NADPH 3 9 NADPH
Glycine Formate AICAR 10
FiGIu formylGIu NADP
6 7 ATP
Glu Glu 8
ADP
5,10–CH –H PteGlu 5–CH=NHH PteGlu 5–CHOH PteGIu Pi 10–CHOH PteGIu n
4
4
2 4 n 4 n n formyl
methylene formimino formyl
ATP
14
6a ADP H O
NH Pi 2
NADP 3 15 de novo biosynthesis
12 of the purine ring
NADPH GAR FGAR
5,10–CH=H PteGlu n
4
methenyl 11
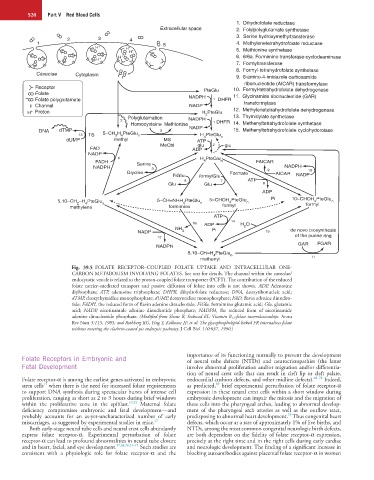
Fig. 39.5 FOLATE RECEPTOR–COUPLED FOLATE UPTAKE AND INTRACELLULAR ONE-
CARBON METABOLISM INVOLVING FOLATES. See text for details. The channel within the caveolae/
endocytotic vesicle is related to the proton-coupled folate transporter (PCFT). The contribution of the reduced
folate carrier–mediated transport and passive diffusion of folate into cells is not shown. ADP, Adenosine
diphosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; DHFR, dihydrofolate reductase; DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid;
dTMP, deoxythymidine monophosphate; dUMP, deoxyuridine monophosphate; FAD, flavin adenine dinucleo-
tide; FADH, the reduced form of flavin adenine dinucleotide; FiGlu, formimino glutamic acid; Glu, glutamic
acid; NADP, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NADPH, the reduced form of nicotinamide
adenine dinucleotide phosphate. (Modified from Shane B, Stokstad EL: Vitamin B 12 -folate interrelationships. Annu
Rev Nutr 5:115, 1985; and Rothberg KG, Ying Y, Kolhouse JF, et al: The glycophospholipid-linked FR internalizes folate
without entering the clathrin-coated pit endocytic pathway. J Cell Biol 110:637, 1990.)
Folate Receptors in Embryonic and importance of its functioning normally to prevent the development
of neural tube defects (NTDs) and neurocristopathies (the latter
Fetal Development involve abnormal proliferation and/or migration and/or differentia-
tion of neural crest cells that can result in cleft lip or cleft palate,
Folate receptor-α is among the earliest genes activated in embryonic endocardial cushion defects, and other midline defects). 68–70 Indeed,
69
71
stem cells when there is the need for increased folate requirements as predicted, brief experimental perturbation of folate receptor-α
to support DNA synthesis during spectacular bursts of intense cell expression in these neural crest cells within a short window during
proliferation, ranging as short as 2 to 3 hours during brief windows embryonic development can impair the mitosis and the migration of
within the proliferative zone in the epiblast. 69,72 Maternal folate these cells into the pharyngeal arches, leading to abnormal develop-
deficiency compromises embryonic and fetal development—and ment of the pharyngeal arch arteries as well as the outflow tract,
75
probably accounts for an as-yet-uncharacterized number of early predisposing to abnormal heart development. Thus congenital heart
miscarriages, as suggested by experimental studies in mice. 57 defects, which occur at a rate of approximately 1% of live births, and
Both early-stage neural tube cells and neural crest cells abundantly NTDs, among the most common congenital neurologic birth defects,
express folate receptor-α. Experimental perturbation of folate are both dependent on the fidelity of folate receptor-α expression,
receptor-α can lead to profound abnormalities in neural tube closure precisely at the right time and in the right cells during early cardiac
and in heart, facial, and eye development. 57,68,70,73–75 Such studies are and neurologic development. The finding of a significant increase in
consistent with a physiologic role for folate receptor-α and the blocking autoantibodies against placental folate receptor-α in women